Figure 1.
Steps of DG and SVZ isolation from the adult mouse brain
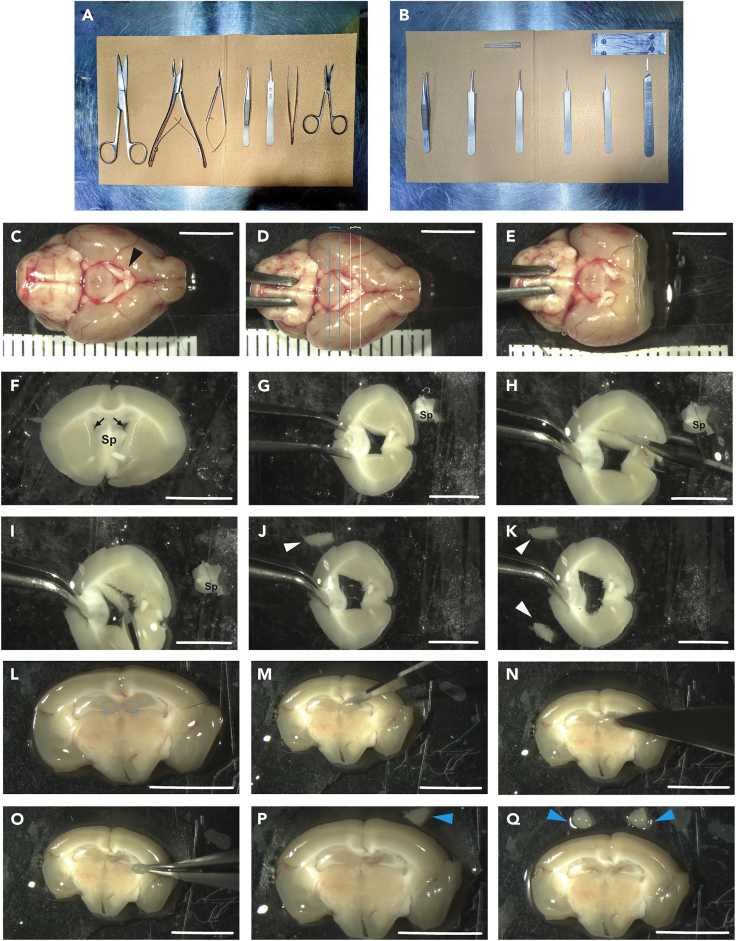
(A) Photograph of the surgery equipment needed for harvest of the adult mouse brain.
(B) Photograph of the surgery equipment for the isolation of the SVZ and DG from harvested adult mouse brain. Note that two separate sets of surgical kit are used to prevent contamination from mouse tissue, hair or other sources.
(C–E) Dissection steps of the adult mouse brain. Through coronal sections the brain is dissected while being placed on its dorsal surface. The black arrowhead points to the Optic chiasm (C), the regions between the white lines and blue lines represent the SVZ and DG isolation sections respectively (D).
(F–K) Steps of SVZ isolation. The black arrows indicate the lateral ventricles (F). Firstly, the septal area (Sp) is removed, followed by dissecting the SVZs each at a time. The white arrowheads show the isolated SVZ tissue (J–F).
Note: the dashed white lines (F and G) represent the SVZ borders bilaterally.
(L–Q) Steps of DG isolation. The dashed blue lines represent the regions of the DG (L). A scalpel (or alternatively a needle 26–27G) is used to gently separate the DG from the surrounding tissue on both right and left sides (M–O). The blue arrowheads show the isolated DG tissue (P-Q).
Note: 1-mm thick sections were measured and used for isolation of both DG and SVZ. Moreover, the use of an angled forceps to fix/stabilize the brain sections during the isolation steps is preferred. Scale bars, 5 mm.