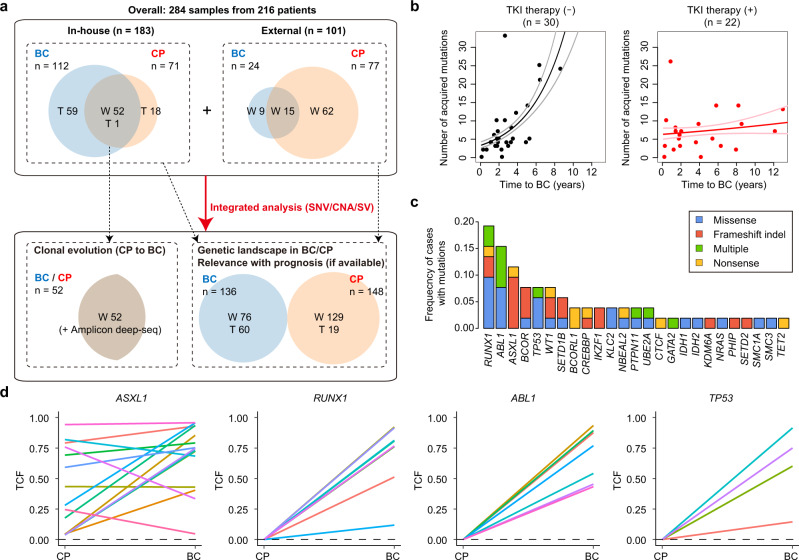
Fig. 1. Somatic mutations acquired during clonal evolution in CML.
a Scheme demonstrating the study cohort. Numbers indicate analysed samples. Numbers in overlapping regions of CP and BC circles indicate the number of cases analysed for both CP and BC. W whole-exome sequencing, T targeted capture sequencing. b Scatter plots for time to progression (horizontal axis) and number of acquired SNVs (vertical axis) during progression from CP to BC in 52 cases for whom WES was performed, using paired CP and BC samples. Regression lines with 95% confidence intervals were also plotted. Cases with or without TKI therapy after CP diagnosis are indicated separately. c Frequencies of mutations acquired during evolution from CP to BC in 52 cases. Recurrently acquired or known driver genes are described. Categories of mutations are depicted in different colours, and “multiple” indicates ≥2 distinct mutations found in the same gene in the same patient. d TCFs of the indicated mutations in the corresponding CP and BC samples determined by conducting deep amplicon sequencing. Black dashed lines indicate a TCF of 0%. Colours represent individual cases.