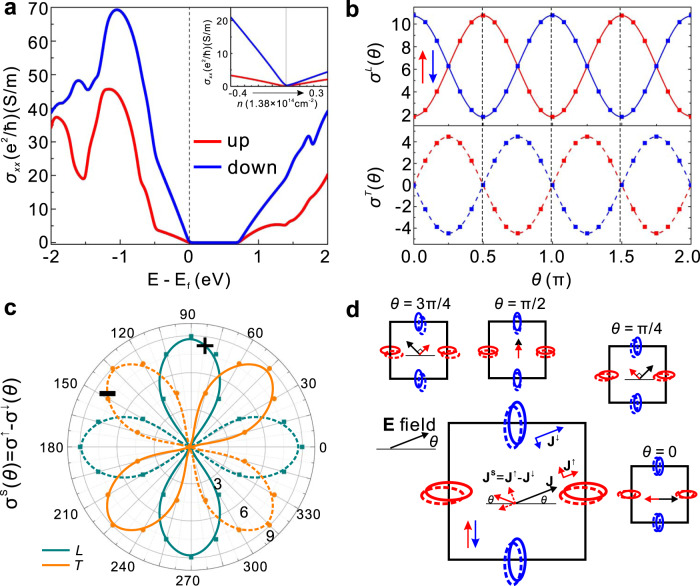
Fig. 4. Angle-dependent spin current and spin Hall effect in monolayer V2Se2O.
a Spin-resolved charge conductivity for electric field along direction. Inset is the dependency of on the carrier density n. For light doping, increases almost linearly with n. b Angle-dependence of the longitudinal (L) and transverse (T) charge conductivity varying with the electric field direction , taken at 0.2 eV below the valance band maximum. The transverse charge conductivity is always opposite for spin-up and spin-down electrons, and hence the transverse charge current is always zero and the charge current direction is always . c The corresponding angle-dependence of the longitudinal and transverse spin conductivity. d Relation between directions of charge current and spin current . The spin current always flows along the direction . In details, for , the spin current will be along the same direction of the charge current, whereas for or , the spin current flow along the opposite direction of the charge current. Moreover, for or , there will be large spin Hall effect, where the spin current is perpendicular to the charge current.