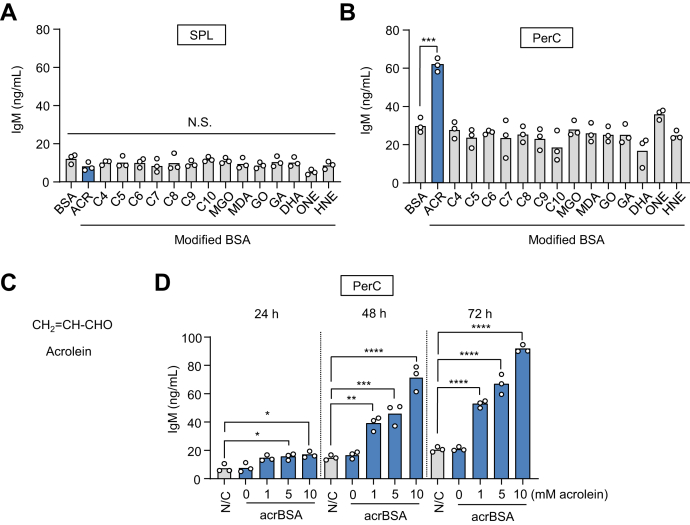
Figure 1.
Stimulation of innate immune response by acrolein-modified proteins. SPL cells (A) and PerC cells (B) prepared from native BALB/c mice were treated with control or modified BSAs with lipid peroxidation–related carbonyl compounds, and the production of IgM was examined. Aldehydes used are ACR, acrolein; C4, crotonaldehyde; C5, 2-pentenal; C6, 2-hexenal; C7, 2-heptenal; C8, 2-octenal; C9, 2-nonenal; C10, 2-decenal; MGO, methylglyoxal; MDA, malondialdehyde; GO, glyoxal; GA, glycolaldehyde; DHA, dehydroascorbic acid; ONE, 4-oxo-2-nonenal; HNE, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Differences were analyzed by Dunnett's test; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; versus BSA. C, chemical structure of acrolein. D, production of IgM by acrBSA in the PerC cells. The cells were treated with control BSA or acrBSA for the times indicated, and the culture supernatants were tested for the production of IgM. acrBSA was prepared by incubating BSA (1.0 mg/ml) with acrolein (0–10 mM) in PBS for 24 h at 37 °C under atmospheric oxygen. The cells were treated with 100 μg/ml protein samples (control or modified BSAs) for 72 h (A and B) or 24 to 72 h (D). Differences were analyzed by Dunnett's test; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; versus BSA (A and B); versus N/C within each time condition (D). acrBSA, acrolein-modified BSA; BSA, bovine serum albumin; IgM, immunoglobulin M; PerC, peritoneal cavity; N.S., no significance; SPL, spleen.