Figure 1.
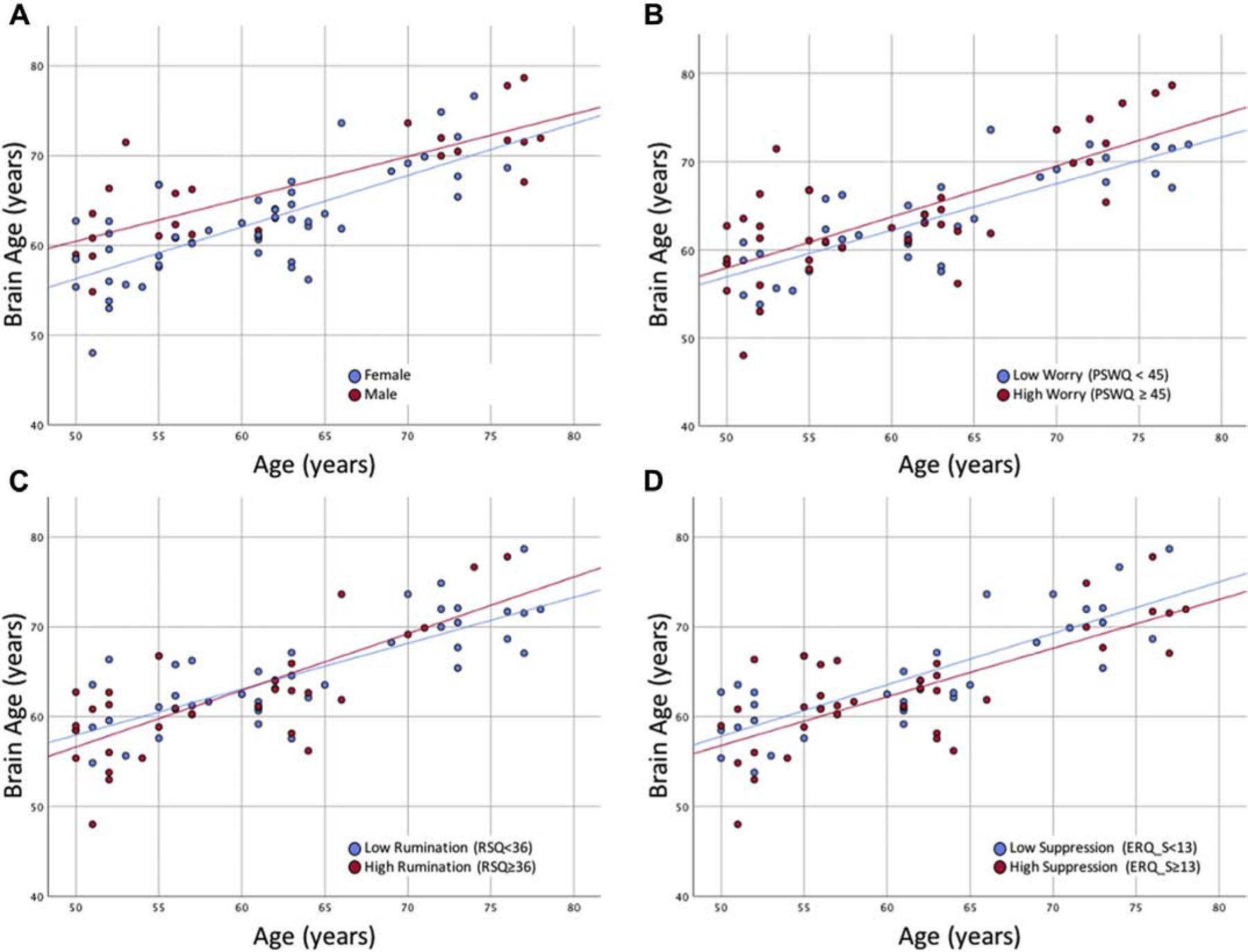
Significant associations between brain age and sex (A), worry (B), rumination (C), and suppression (D) adjusting for chronological age. Cutoffs for PSWQ, RSQ, and ERQ suppression were based off of the medians of the sample as these are meant to illustrate associations that utilized continuous measures. Greater brain age is associated with greater age, being male (compared to female), greater worry, greater rumination, and lower suppression.
