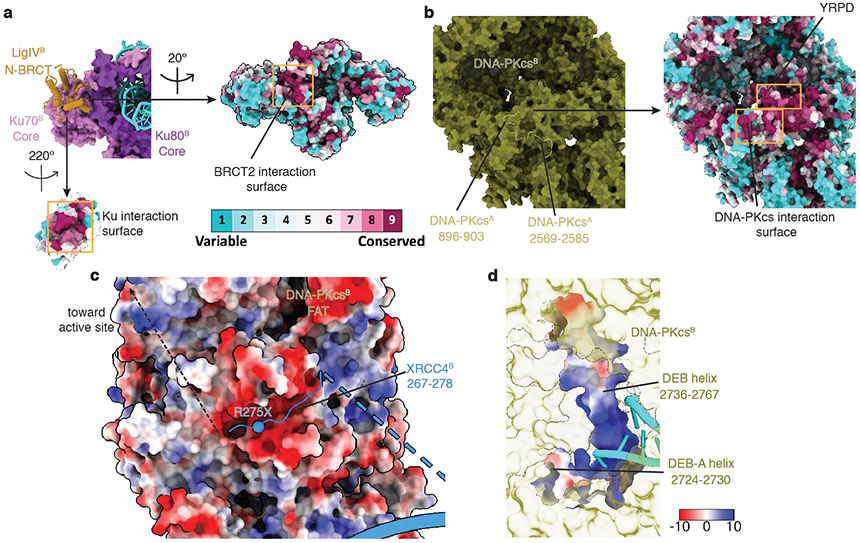
Extended Data Fig. 5. Surface electrostatic potential and conservation of different areas in the LR synaptic complex.
a, Close-up view of the interaction surface between LigIV N-BRCT domain and Ku70 vWA domains colored by sequence conservation. b, Close-up view of the DNA-PKcs-DNA-PKcs interaction surface colored by sequence conservation. c, Surface electrostatic potential view of DNA-PKcs near its FAT domain, showing its negatively charged interface between XRCC4 C-terminal region (ribbon). The approximate path of the XRCC4 C-terminal peptide containing multiple phosphorylation sites is depicted. The sphere depicts the location of a cancer-associated truncation mutation that occurs at the interface. d, Surface electrostatic potential view of DNA-PKcs DEB and DEB-A helix. The DNA-interaction surface is positively charged. When models are not colored by either surface electrostatic potential or sequence conservation, the color codes are the same as in Fig. 1. We cannot rule out the unlikely possibility that the stabilization of the DEB helix is due to the presence of a 3’ overhang that existed in our DNA substrate design (Extended Data Fig. 1g).