Fig. 1.
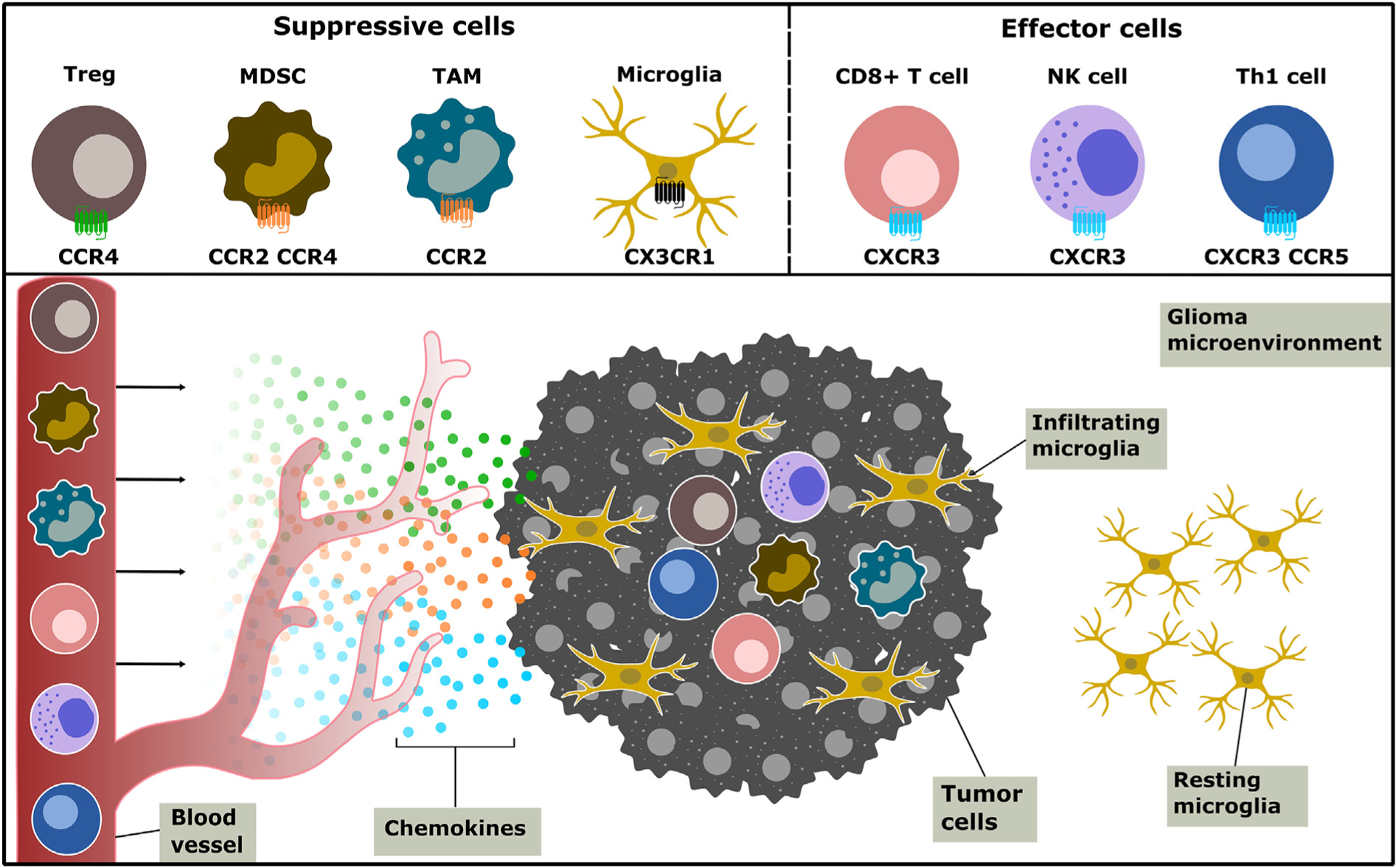
Chemokines shape the glioma immune landscape by recruiting chemokine receptor-expressing immune cells to the glioma microenvironment. Pro-tumor immune-suppressive cells Tregs, MDSCs, and TAMs are honed from the periphery to the site of the tumor through a variety of chemokine receptors, such as CCR2 and CCR4. Anti-tumor immune cells, including CD8+ and Th1 T cells and NK cells, infiltrate the tumor microenvironment and illicit tumor-killing mechanisms. These effector cells express the chemokine receptor CXCR3. CX3CR1-expressing microglia, a CNS resident macrophage, make up the bulk of the glioma infiltrating immune cells and may exhibit both pro- and anti-tumor effects.
