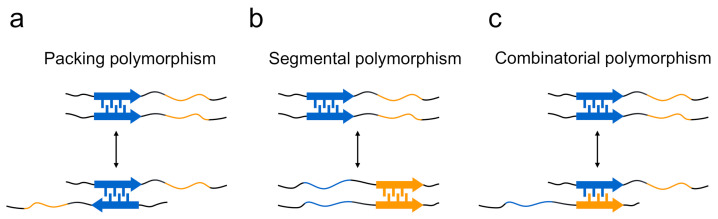
Figure 4.
Three proposed models explaining the formation mechanism of polymorphs in terms of steric zippers. (a) Polymorphs are produced when steric zippers are formed with different packing patterns or with different interfaces between the same pair of segments (i.e., packing polymorphism). (b) In the case of polypeptide chains that contain several different segments with high propensity to form steric zippers, the difference in region of steric zippers is another mechanism for forming polymorphs (i.e., segmental polymorphism). (c) Additionally, differences in the sequences of paired polypeptide segments also contribute to the formation of polymorphs (i.e., combinatorial polymorphism).