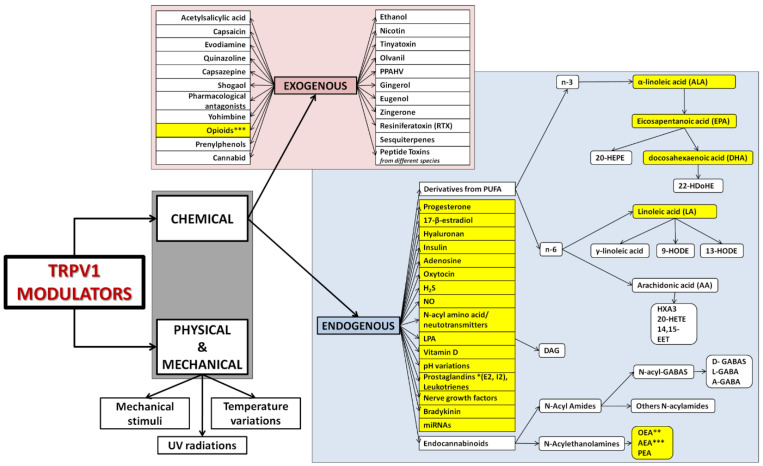
Figure 4.
Modulators of TRPV1 function. The schema shows most of the activators and modulators of TRPV1 function investigated to date, divided into two main groups: physical and physical stimuli; and chemical activators. Physical and mechanical modulators include temperature variations (heat or cold) [34], UV radiation [35,36], and mechanical stimuli [37]. The chemical activators group is divided in turn into two subgroups depending on the origin of the activator/modulator: exogenous and endogenous. Exogenous stimuli are capsaicin [38] and its antagonist capsazepine [39], resiniferatoxin (RTX) [37,40], bradykinin [41], yohimbine [42], ethanol [43], evodiamine [44], 17-β-estradiol [45], quinazoline [46], progesterone [47], numerous opioids [48], nicotine [49], hyaluronan [50], insulin [51], tinyatoxin [52], olvanil [53], acetylsalicylic acid [54], eugenol [55], sesquiterpenes [56,57,58], cannabidiol [59], prenylphenols [60], zingerone [61], shogaol [61], PPAHV [62], gingerol [63], numerous pharmacological antagonists [64,65,66,67], and peptide toxins from different species [4,68]. Endogenous activators comprise numerous compounds [1], such as the wide family derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). According to the position of the first double bond present in their structures, this big family can be divided into n-3 (α-linolenic acid (ALA) and its products eicosapentanoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), 20-hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acid (20-HEPE) and 22-hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acid (22-HDoHE)), and n-6 linoleic acid (LA) and its products γ-linoleic acid, arachidonic acid (AA) [69] (which produces hepoxylin, HXA-3, 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid, 14,15-EET, and 20-hydroxyeicosatetranoic acid, 20-HETE), 9- and 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acids (9-HODE and 13-HODE). Other agonists endogenously secreted are oxytocin [70], adenosine [71], nitric oxide [72], hydrogen sulfide (H2S) [73], lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) [74] and its derivative diacylglycerol [75], pH variations [76,77], vitamin D [78], N-acyl amino acids/neurotransmitters [79], miRNAs [80,81], prostaglandins, nerve growth factors and the endocannabinoids family, including N-Acyl amides [82] (N-acyl GABAS [83,84] derived then in D-GABAs, L-GABA and A-GABA) and N-acylethanolamines (NAEs) [85], such as anandamide (AEA) *** [86], oleylethanolamine (OEA) [87] and palmitoylethanolamine (PEA) [88]. * Product from arachidonic acid. ** Derived also from oleic acid, identified as a TRPV1 natural inhibitor [89]. *** Can be exogenous and endogenous. Compounds evidenced in yellow have been found to produce an effect also in spermatozoa, being synthesized by them or present in the oviductal fluid or female reproductive tract.