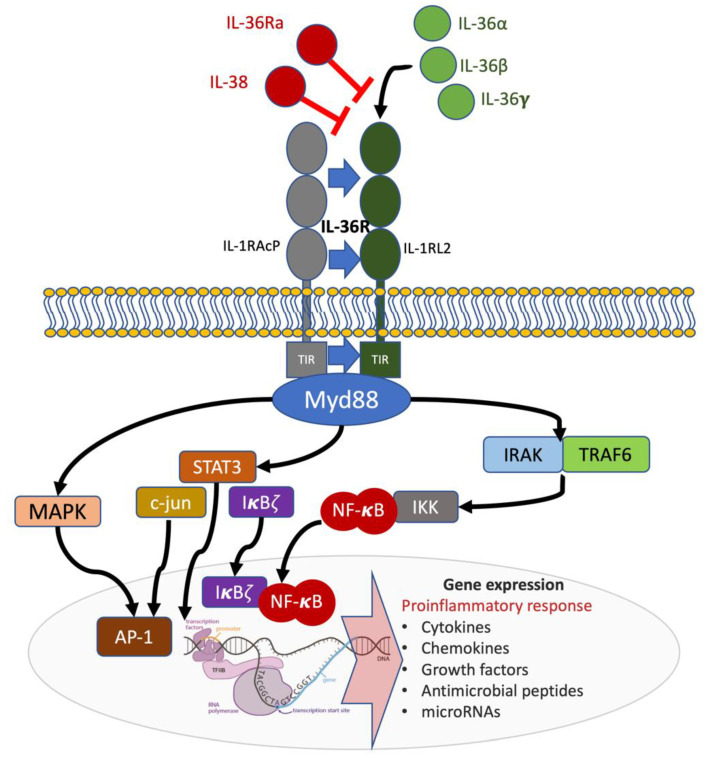
Figure 1.
Receptor and signaling pathways involved in the IL-36 axis. IL-36R is a heterodimeric complex composed of an IL-1RL2 subunit and IL-1RAcP co-receptor. Agonist binding (IL-36α, IL-36β or IL-36γ) to IL-1RL2 results in IL-1RAcP recruitment and the activation of intracellular pathways. The MyD88/IRAK1/IRAK2/TRAF6 platform with corresponding intracellular signaling results in pro-inflammatory gene expression. Antagonism by IL-36Ra and IL-38 inhibits IL-36R signaling (shown in red). TIR: Toll/interleukin-1 receptor; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response (88); NF-kB: nuclear factor kB; IRAK: Interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase; TRAF: TNF receptor-associated factor; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.