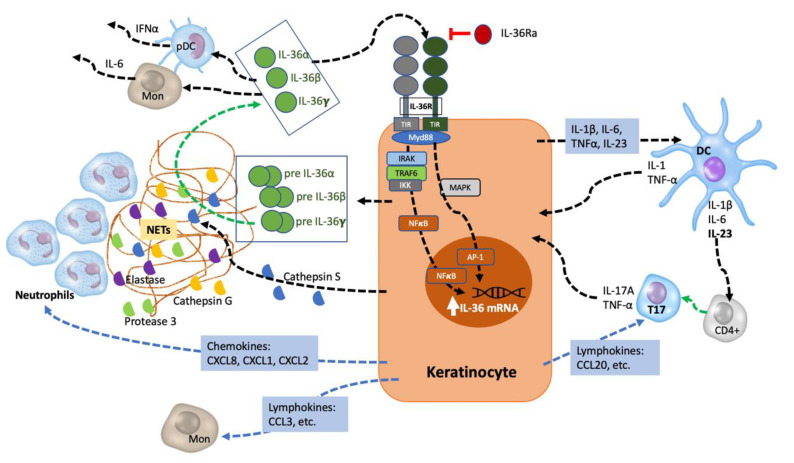
Figure 2.
IL-36 autocrine and autoinflammatory circuits. IL-1, TNF, and IL-17A induce IL-36 expression by KCs. IL-36 cytokines are secreted as precursors that require processing by neutrophil-derived proteases (elastase, cathepsin G, or protease 3) and KC-derived cathepsin S. Mature IL-36 cytokines bind to IL-36R on the KC cell surface, acting in an autocrine manner to further induce IL-36 expression. Moreover, they promote the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-12, IL-23, IL-6, and TNF-α), neutrophil chemokines (CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL6, and CXCL8 [(IL-8)], lymphokines (such as CCL20, CCL3) and co-stimulatory molecules by DCs and Th1. They also induce T-cell proliferation, and cytokines secreted by infiltrating Th1 and Th17 lymphocytes further potentiate this inflammatory loop by inducing IL-36 expression and other pro-inflammatory mediator production by KCs. Mon: monocytes; pDC: plasmatic dendritic cell; TIR: Toll/interleukin-1 receptor.