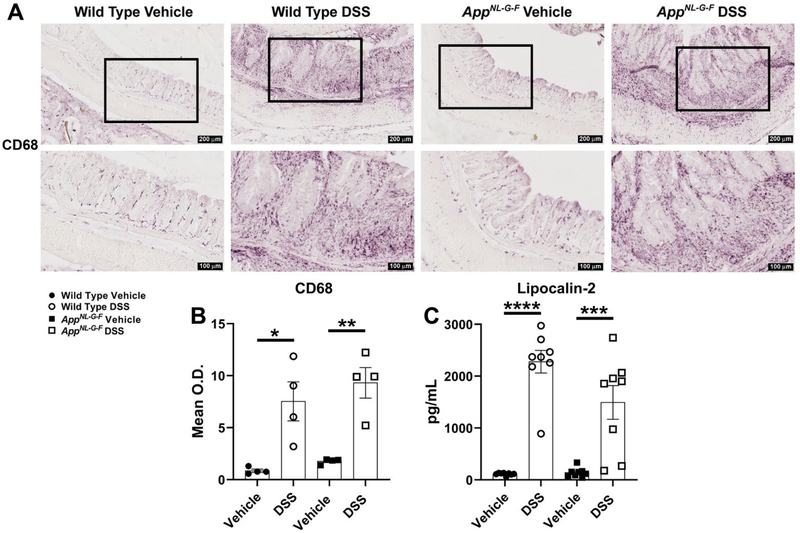
Fig. 4.
DSS treatment led to infiltration of macrophages and increased levels of an inflammatory marker in the colon. (A) Representative anti-CD68 immunostaining of cross sectional Swiss-rolls of the distal colon are shown with 10X and 20X magnifications. (B) CD68 mean optical density was measured using colon sections of DSS treated vs. vehicle groups in both genotypes, (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, unpaired two-tailed t-test indicate WT CD68 t(6)=3.547 and p=0.0121; AppNL-G-F CD68 t(6)=5.112 and p=0.0022, mean ± SEM, n= 4 Swiss-rolls/condition/genotype). (C) The changes in lipocalin-2 levels, as an anti-microbial siderophore-binding peptide involved in IBD, were assessed to determine the extent of intestinal inflammation in both the WT and AD mouse model following DSS exposure, (***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, unpaired two-tailed t-test indicate WT lipocalin-2 t(14)=9.931 and p<0.0001; AppNL-G-F lipocalin-2 t(14)=4.151 and p=0.0010, mean ± SEM, n=8 animals).