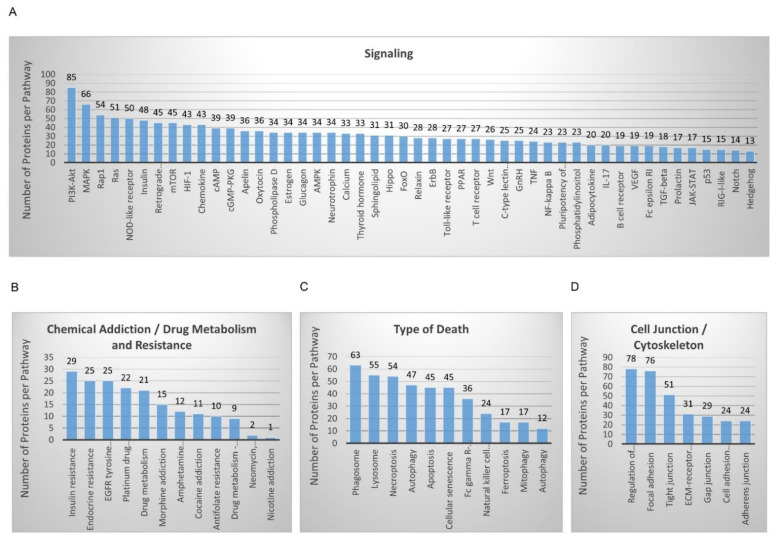
Figure 1.
Dissection of WM115 deep proteome components in diverse functional networks. (A) “Signaling”. (B) “Chemical Addiction/Drug Metabolism and Resistance”. (C) “Type of Death”. (D) “Cell Junction/Cytoskeleton”. (A–D) KEGG was employed as the suitable bioinformatics tool for the analysis. The number of proteins in the identified sub-routines (pathways) are shown on the top of the respective bars. (A) “PI3K-AKT”, “MAPK”, “RAP1”, “RAS”, “NOD-like receptor”, “Insulin”, “Retrograde Endocannabinoid”, “mTOR”, “HIF-1”, “Chemokine”, “cAMP”, “cGMP-PKG”, “Apelin”, “Oxytocin”, “Phospholipase D”, “Estrogen”, “Glucagon”, “AMPK”, “Neurotrophin”, “Calcium”, “Thyroid hormone”, “Sphingolipid”, “HIPPO”, “FOXO”, “Relaxin”, “ERBB”, “TOLL-like receptor”, “PPAR”, “T cell receptor”, “WNT”, “C-type Lectin receptor”, “GnRH”, “TNF”, “NF-kappa B”, “Pluripotency of stem cells”, “Phosphatidylinositol”, “Adipocytokine”, “IL-17”, “B cell receptor”, “VEGF”, “Fc epsilon RI”, “TGF-beta”, “Prolactin”, “JAK-STAT”, “p53”, “RIG-I-like”, “NOTCH”, and “HEDGEHOG”. (B) “Insulin resistance”, “Endocrine resistance”, “EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance”, “Platinum drug resistance”, “Drug metabolism”, “Morphine addiction”, “Amphetamine addiction”, “Cocaine addiction”, “Antifolate resistance”, “Drug metabolism—Cytochrome P450”, “Neomycin, Kanamycin and Gentamicin biosynthesis”, and “Nicotine addiction”. (C) “Phagosome”, “Lysosome”, “Necroptosis”, “Autophagy—animal—Homo sapiens (human)”, “Apoptosis”, “Cellular senescence”, “Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis”, “Natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity”, “Ferroptosis”, “Mitophagy”, and “Autophagy—other—Homo sapiens (human)”. (D) “Regulation of Actin cytoskeleton”, “Focal adhesion”, “Tight junction”, “ECM-receptor interaction”, “Gap junction”, “Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)”, and “Adherens junction”. Due to their specific functional traits, certain proteins are classified in more than one pathway.