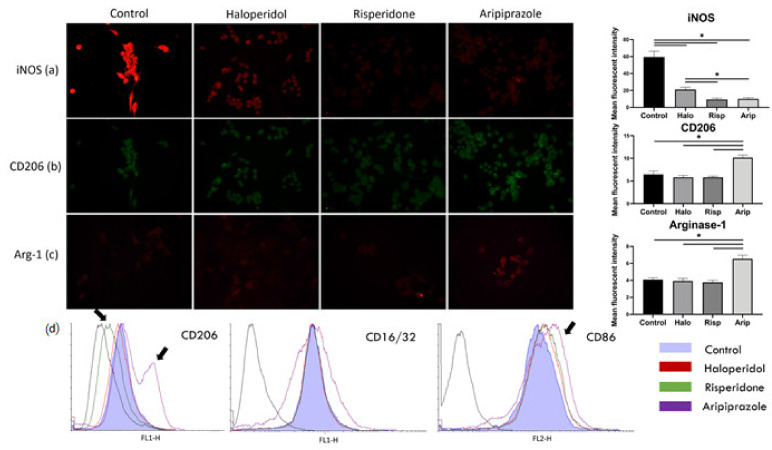
Figure 2.
Effect of antipsychotics on inflammatory and metabolic phenotype markers. Expression of microglia polarization markers was assessed using immunofluorescence and flow cytometry. Control BV-2 microglial cells exhibited a high expression of iNOS, with low expressions of CD206 and Arg-1, constituting a pro-inflammatory phenotype (a). Administering antipsychotics led to a marked reduction in iNOS expression in all three tested substances (p < 0.0001), with most significant reductions upon administration of risperidone (p < 0.0001) and aripiprazole (p < 0.0001) (a). CD206 (b) and Arg-1 (c) expressions only increased when the cells were stimulated with aripiprazole (p < 0.0001). Similar was observed with flow cytometry (d), where aripiprazole administration led to an increase in cells expressing CD206 and CD86 (marked with black arrows). On the other hand, risperidone decreased the expression of CD206 in cells on flow cytometry (marked with black arrows). * Statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05 values.