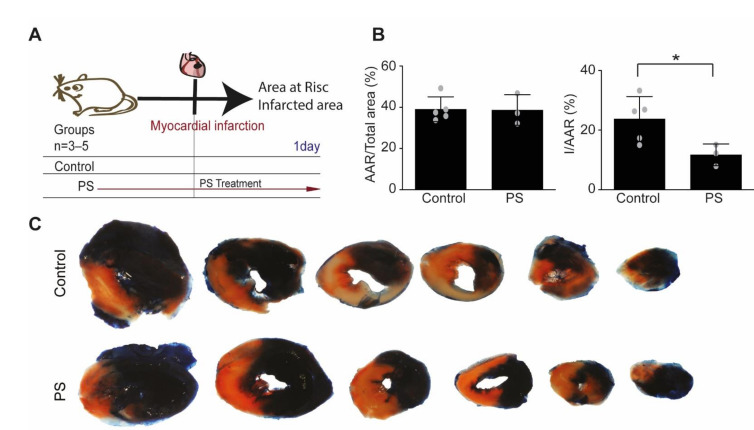
Figure 1.
Phosphatidylserine oral supplementation before ischemia-reperfusion confers cardio-protection against acute myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. (A) Mice were randomly assigned to 2 treatment groups: (1) Control (n = 5): saline vehicle control by daily oral gavage one week prior to ischemia-reperfusion injury and until end of experiment; (2) PS group (n = 3): phosphatidylserine was given by daily oral gavage for one week prior to ischemia-reperfusion injury and until the end of experiment; Samples were collected and analyzed one day after ischemia-reperfusion to avoid inflammatory and remodeling interferences. (B) There was no difference in the size of the area at risk (AAR) between the two treatment groups. PS treatment reduced MI size (I) as a percentage of the AAR. (n = 3–5, unpaired Student’s-t test, * p < 0.05, Values ± SD). (C) Representative heart sections from both groups are shown (white represents infarcted myocardium, red represents viable myocardium from area of risk, blue represents non-ischemic areas).