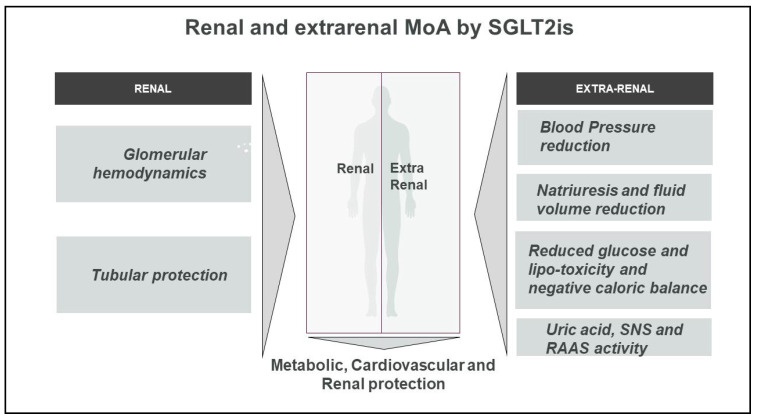
Figure 1.
Renal and extrarenal mechanisms of action by SGLT2is. Selective inhibition of SGLT2 in proximal renal tubule prevents glucose reabsorption and entails several potentially favorable effects. Glycosuria concurs to euglycemia, lowers HbA1c, and reduces glucotoxicity, preserving beta cell function. As for extra-glycemic effects, SGLT2is promote diuresis and natriuresis and determine a mild reduction in extracellular fluid, especially interstitial fluid. Effective blood volume and blood pressure reduction ensues. Abbreviations: MoA, mechanisms of action; RAAS, renin angiotensin aldosterone system; SNS, sympathetic nervous system.