FIGURE 4:
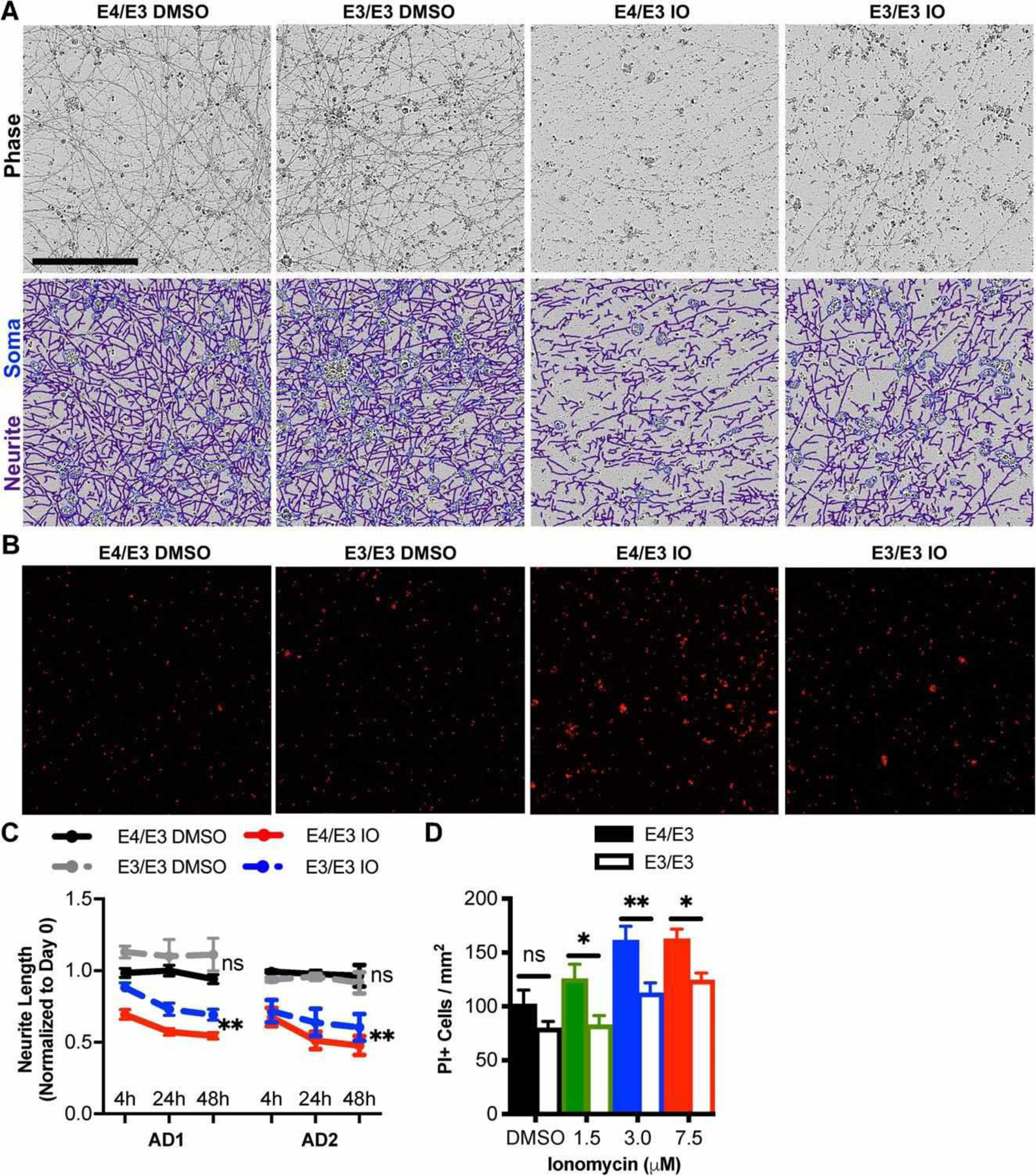
Genetic editing of E4 to E3 protects neurons from ionomycin-induced toxicity. (A) Phase contrast images of apolipoprotein E (APOE)-isogenic neurons were captured 0, 4, 24, and 48 hours after treatment with ionomycin (IO) or dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) vehicle. Depicted are representative phase contrast images at 24 hours and corresponding neurite (purple) and cell body (blue) masks beneath. Scale bar = 200 μm. (B) Propidium iodide (PI) epifluorescence labeling dead cells were counted after cultures were treated for 48 hours with 1.5, 3.0, or 7.5 μM IO or DMSO vehicle. Depicted are representative images treated with 7.5 μM IO or DMSO vehicle. (C) Quantitation of neurite lengths from A. There were n = 4 independent treatments per genotype and patient background. Each data point is the average of 3 fields per treatment. The statistical test was a 2-way repeated measures analysis of variance for interaction between APOE genotype and time for each drug treatment: **p < 0.01; ns = not significant. Not all statistical comparisons are shown for clarity. (D) Quantitation of dead cells from B. There were n = 12 independent treatments per concentration and genotype. The statistical test was 2-way analysis of variance followed by Sidak multiple comparison test for each concentration: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
