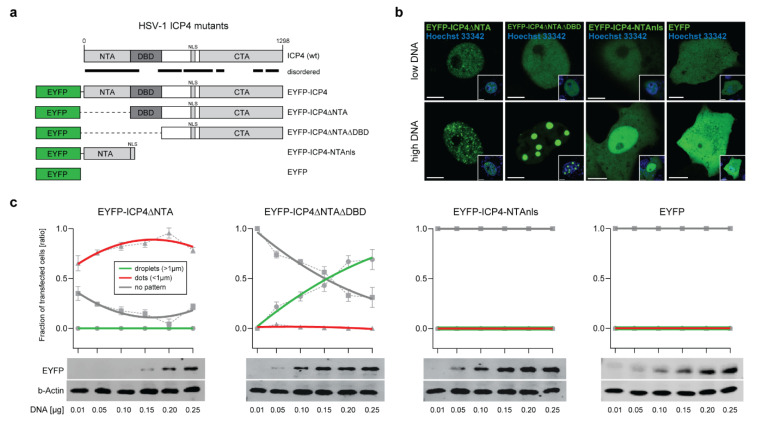
Figure 3.
The ICP4 NTA and DBD control the protein phase behavior. (a) Schematic representation of the mutant HSV-1 ICP4 constructs used in this study. The plasmid expressing EYFP-ICP4 was used as a positive control and the plasmid expressing EYFP alone was used as a negative control. Disordered regions are indicated with black lines. (b) Phase behavior of the mutant ICP4 constructs. Vero cells were transfected with either 0.01 µg (low DNA) or 0.15 µg (high DNA) plasmid DNA expressing the ICP4 constructs described in panel 3a. The cells were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 at 16 hpt (small inset) and subjected to live-cell imaging using CLSM. Representative images for each construct are shown. Scale bars: 5 µm (EYFP-ICP4 constructs) and 10 µm (EYFP). (c) Live-cell phase diagrams of the mutant ICP4 constructs. The generation of the protein phase diagrams was performed as described for the EYFP-ICP4 construct (see Figure 1d). The Western blot analysis to detect all mutant ICP4 constructs was performed using a monoclonal antibody against GFP (JL-8) that is capable of detecting EYFP (EYFP). The beta-actin protein levels served as a loading control (b-Actin).