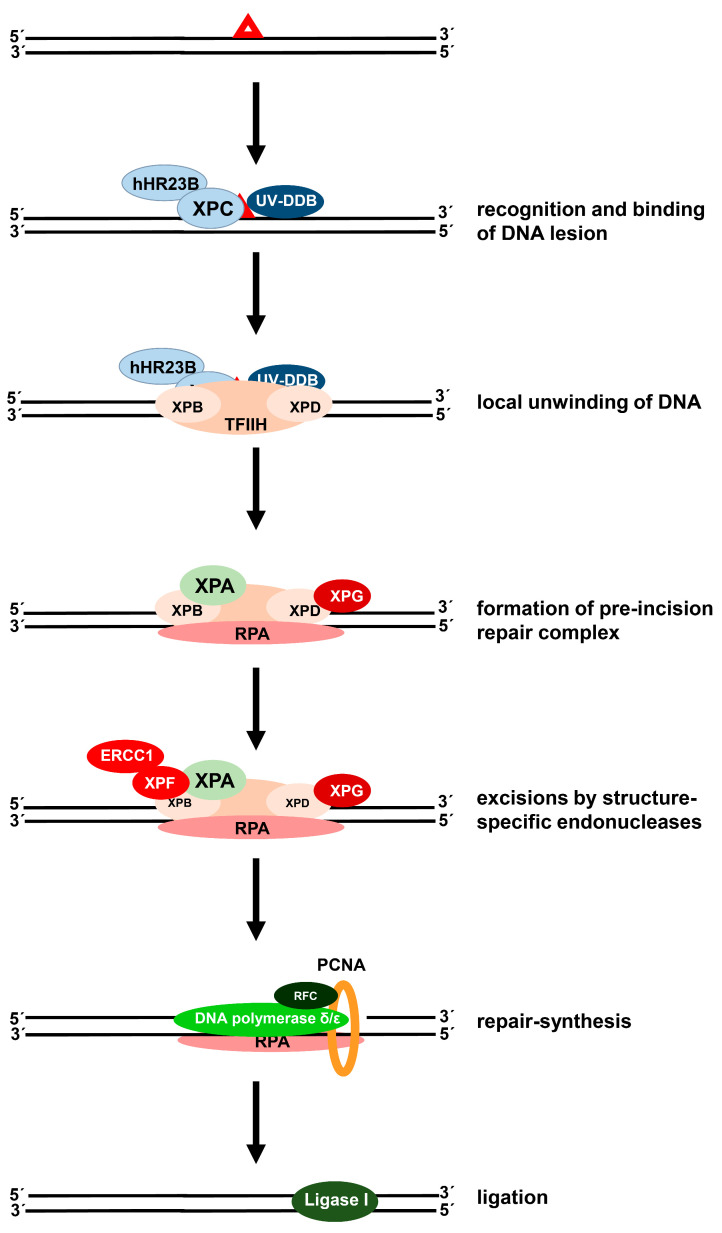
Figure 2.
Mechanism of human nucleotide excision repair. The repair proteins XPC-hHR23B and UV-DDB detect and bind to the DNA lesion (red triangle). The transcription factor TFIIH with its helicase subunits XPB and XPD is recruited to the damage, leading to local unwinding of the DNA around the lesion. A pre-incision complex is formed by recruitment of XPA, RPA, and XPG, followed by incisions on both sides of the damage, mediated by the endonucleases XPG and ERCC1-XPF complex. DNA polymerase δ/ε, supported by PCNA and RFC, catalyze DNA re-synthesis, the nick is sealed by DNA ligase I.