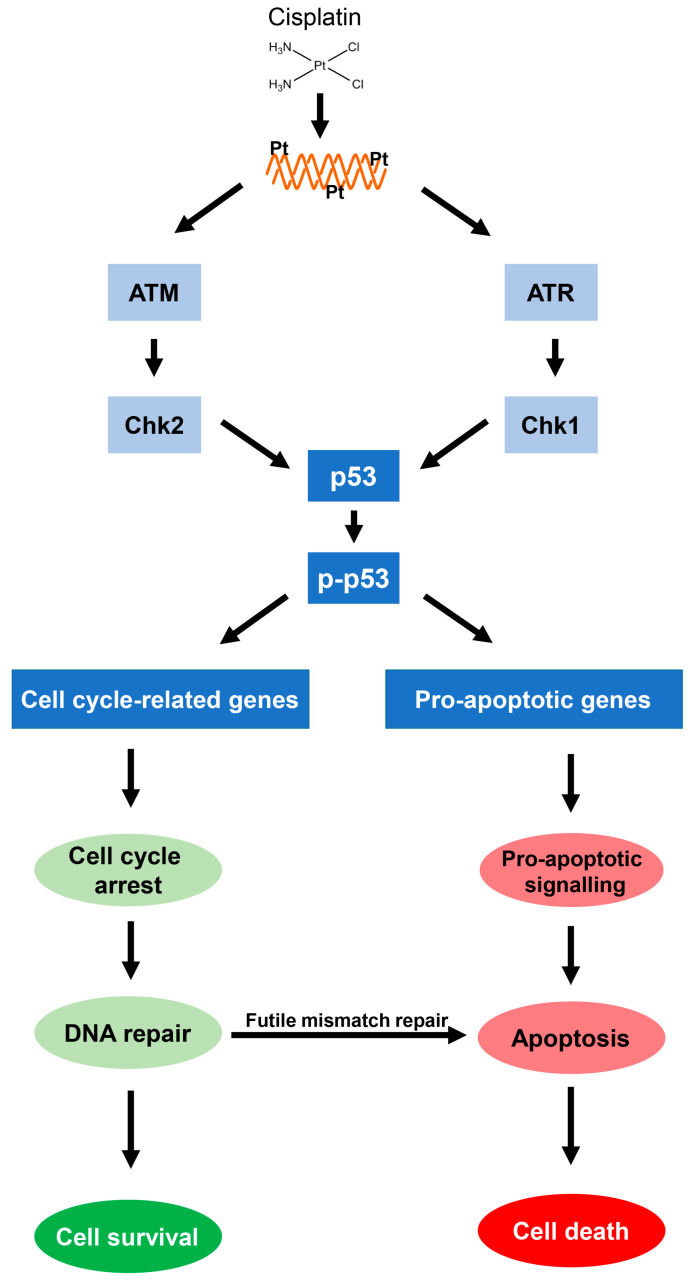
Figure 4.
The p53-mediated DNA damage response. Cisplatin-induced DNA damage activates ATM/Chk2 and/or ATR/Chk1, which leads to phosphorylation of p53. Activated p53 induces expression of genes related to the cell cycle control allowing time for DNA repair. If the amount of damage exceeds the cellular repair capacity, apoptosis-related genes will be expressed leading to apoptotic cell death. Futile mismatch repair (MMR) also contributes to cisplatin-induced apoptosis.