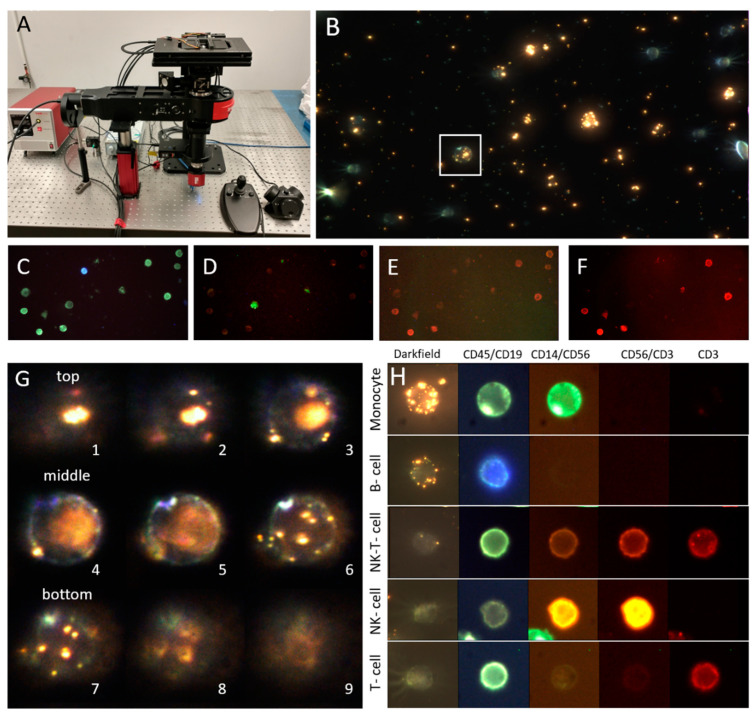
Figure 1.
Microscopy system and example images of PBMC from a healthy control. (A) Combined automated darkfield and epi-fluorescence microscope developed for the project. (B) Maximum-intensity projection of the z-stack darkfield image of a field of view. Some cells show PNPs bound to them. (C) First fluorescent channel showing all PBMC in green (CD45) and B cells in blue (CD19). (D) Second fluorescent channel showing monocytes in green (CD14) and NK cells in orange (CD56). (E) Third fluorescent channel showing NK cells in orange (CD56) and T cells in red (CD3). (F) Fourth fluorescent channel showing T cells in red (CD3). (G) Representative slices of the z-stack of the monocyte highlighted in B. Please observe how PNPs are visible on the planes of the cell that are above (top) and below (bottom) its equatorial plane (middle), located in the center of the inset. This is due to the high brightness of the plasmonic nanoparticles and the transparency of the cells under darkfield. Numbers indicate the order of the image in the z-stack. (H) Composite image showing the darkfield maximum-intensity projection and 4-channel fluorescence of example cells of different lineages. Please observe how, for these examples, the monocyte exhibits high CA125 binding, the B-cell medium CA125 binding and other cell classes show no binding.