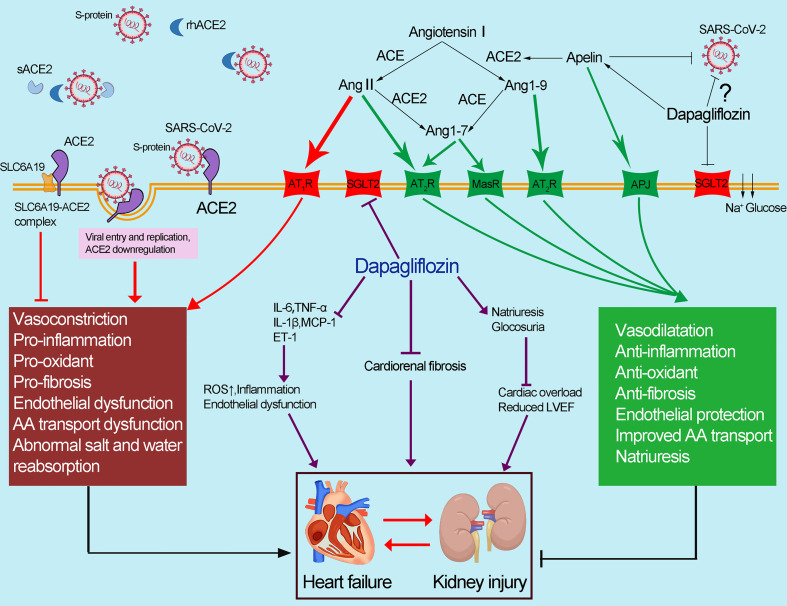
Fig. 4.
Abnormal apelin-ACE2 and SGLT2 signaling contribute to adverse cardiorenal injury in patients with COVID-19. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds to membrane-bound ACE2, resulting in the downregulation of ACE2. Downregulation of ACE2 results in the accumulation of Ang II, contributing to the deleterious effects in COVID-19 (marked in red). ACE2 could catalyze Ang II conversion to Ang-(1–7), which exerts its cardiorenal protective effects including anti-inflammation, antioxidant and antifibrosis (marked in green). Dapagliflozin has a protective effect against the cardiorenal injury through improving the abnormal apelin-ACE2 signaling, indicating that SGLT2 inhibitors, apelin and rhACE2 could be potential therapeutic approaches in COVID-19 patients with adverse cardiorenal injury. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)