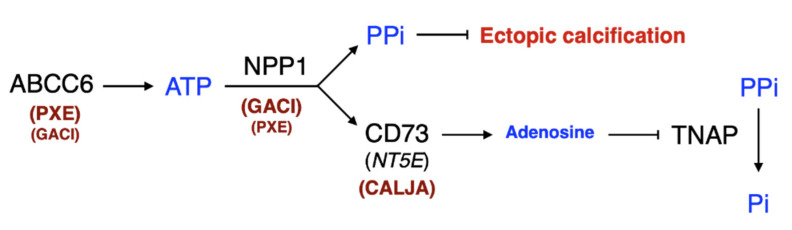
Figure 1.
The ABCC6 pathway influences calcification and extracellular purinergic metabolism. ABCC6 facilitates the cellular efflux of ATP from liver and other tissues/cells, which is quickly converted to pyrophosphate (PPi), a potent inhibitor of mineralization. Decreased plasma PPi levels cause calcification in PXE and GACI. CD73 activity leads to adenosine production, which affects many biological activities including the inhibition of TNAP synthesis. TNAP degrades PPi into inorganic phosphate (Pi), an activator of calcification, which leads to vascular calcification in CAL JA patients.