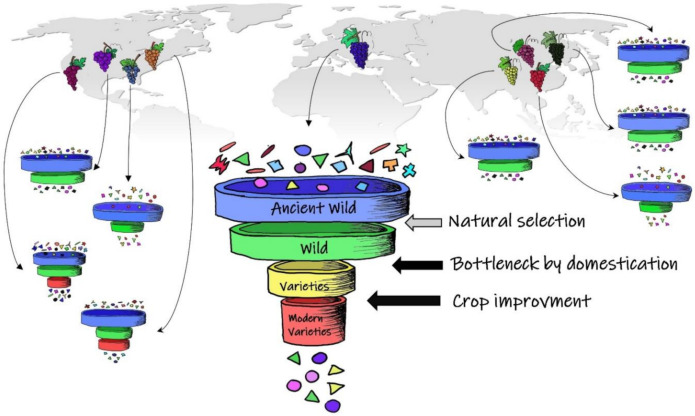
Figure 4.
Grapevine is originated from an ancient wild progenitor. Although it has suffered from a weak bottleneck and the breeding have maintained a high level of heterozygosity, several resistance or tolerance genes could be lost during the evolution. The funnel shows the reduction of genetic diversity in time (different shapes indicate different classes of genes and different colours indicate different alleles). Natural selection (horizontal grey arrow) caused by climate changes in the past and artificial selection (horizontal black arrows) caused by human activity more recently can have driven the loss of genes and alleles. On the other hand, the wild American and Asian grapes are adapted to a wide range of climatic conditions and have suffered minor effects from human activity, thus they can harbour several resistance or tolerance genes. The assembly of a pangenome offers the possibility to recover and collect the original gene diversity conserved in wild and domesticated grapes.