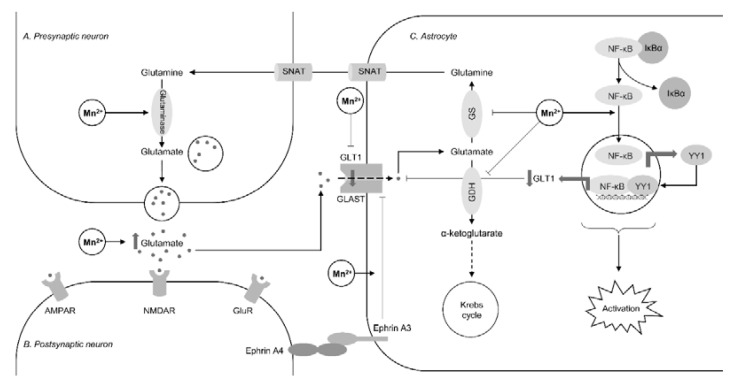
Figure 4.
The impact of manganese overexposure on glutamate-glutamine cycle. Manganese exposure results in a significant increase in glutamate levels through down-regulation of glutamine synthetase (GS) [179] and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) [182] along with up-regulation of glutaminase [179]. These effects result in reduced glutamate-to-glutamine conversion as well as glutamate catabolism in Krebs cycle through the formation of α-ketoglutarate. Mn-induced inhibition of astrocyte glutamate uptake results from inhibition of glutamine transporters (GLT1 and GLAST). Recent studies demonstrated that this inhibitory effect may be mediated through NF-κB-dependent activation of Yin Yang 1 (YY1) transcription factor [173] and ephrin A3 [178]. It is also notable that Mn-induced NF-κB signaling also plays a significant role in astrocyte activation associated with reduced glutamine synthetase activity [181].