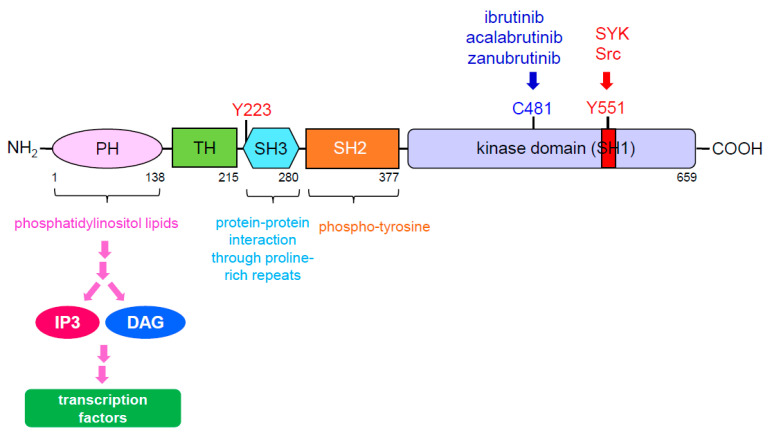
Figure 2.
BTK domain diagram. BTK contains five domains, including a PH domain at the amino terminus, a TH domain, a SH3 domain, a SH2 domain and a tyrosine kinase domain at the carboxyl terminus. The PH domain of BTK is able to interact with phosphatidylinositol lipids which allows it to eventually regulate transcription factors through IP3 and DAG. The SH3 domain of BTK mediates protein-protein interactions through proline-rich repeats and also contains a tyrosine at 223 position (Y223), an autophosphoryaltion site of BTK. The SH2 domain of BTK can interact with phospho-tyrosine. The kinase domain of BTK, also known as the SH1 domain contains a tyrosine at 551 position (Y551) with the activation loop. Once Y551 is phosphorylated by SYK or Src, it results in autophosphrylation of Y223 to fully activate BTK. In addition, cysteine 481 (C481) is the site to which BTK inhibitors covalently bound. Abbreviation: PH: pleckstrin homology; TH: Tec homology; SH: Src homology; IP3: inositol triphosphate; DAG: diacylglycerol.