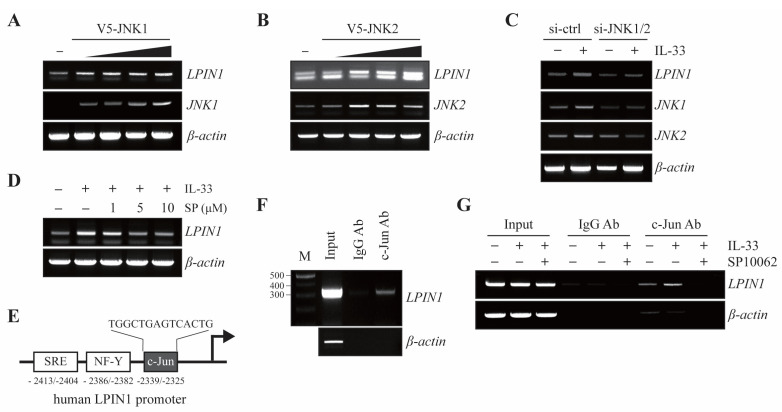
Figure 4.
IL-33 stimulates binding of c-Jun to the LPIN1 promoter. (A,B) MCF7 cells were transfected with different amounts of pcDNA4/V5-JNK1 (A) or pcDNA4/V5-JNK2 (B), incubated for 48 h, harvested, and subjected to immunoblotting. The levels of LPIN1 and β-actin mRNA were determined using RT-PCR. (C) MCF7 cells were transfected with siRNA-JNK1/2. At 48 h after transfection, the cells were serum starved for 24 h, treated with 25 ng/mL IL-33 for 24 h, harvested, and lysed. The levels of mRNA were determined using RT-PCR. (D) MCF7 cells were serum starved for 24 h, pretreated with the indicated concentrations of SP600125 for 2 h, and then exposed to 25 ng/mL IL-33 for 24 h, harvested, and lysed. The levels of mRNA were determined using RT-PCR. (E) Schema of the putative c-Jun-binding sites within the LPIN1 promoter region. (F) ChIP assay with either anti-c-Jun antibody or control mouse IgG, with input chromatin as a positive control. (G) Cells were serum starved for 24 h, pretreated with the indicated concentrations of SP600125 for 2 h, and then exposed to 25 ng/mL IL-33 for 24 h. Following that, the ChIP assay was performed on these samples using an anti-c-Jun antibody or control mouse IgG, with input chromatin as a positive control. The input DNA and DNA isolated from the precipitated chromatin were amplified using PCR and separated on a 1.5% agarose gel. IgG, immunoglobulin.