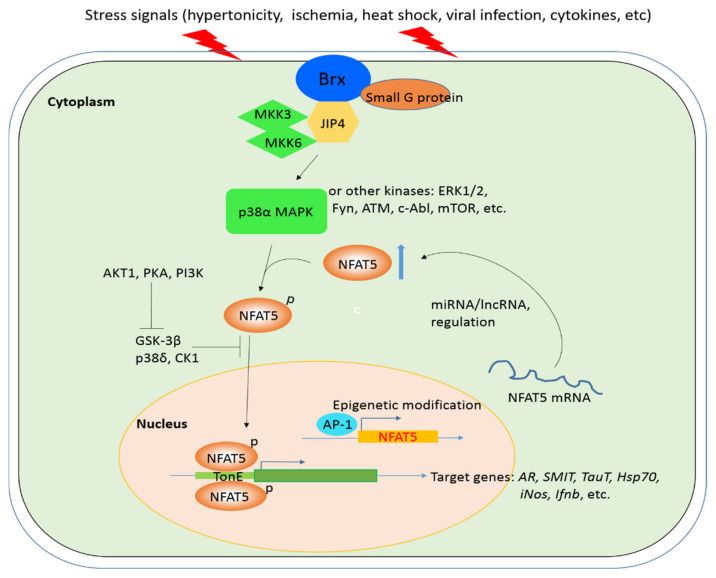
Figure 1.
NFAT5-mediated signaling pathways under various cellular stress conditions. The various extracellular stress signals caused by hypertonic or non-hypertonic condition activate signal pathways largely through the Brx, which forms the complex with small G-protein, JIP4 and kinases MKK3/6. The complex then activates p38α-NFAT5 cascade via phosphorylation by MKK3/6. Other kinases can also phosphorylate and activate NFAT5. The phosphorylated NFAT5 translocates into nucleus, binds the TonE site of target gene promoter and initiates transcription of its target genes that response to their corresponding stimuli. Furthermore, GSK-3β, p38δ and CK1 inhibit NFAT5 activation and nuclear localization; however, AKT, PKA and PI3K can suppress the inhibitory effect of GSK-3β on NFAT5 activation by phosphorylation. In addition to kinases, other factors such as miRNA, lncRNA and epigenetic modification also regulate the AP-1-mediated NFAT5 expression and play a role in NFAT5 activation. Thin arrow: promotion; blue thick arrow: upregulation; T-shaped inhibitory arrow: inhibition. Brx: Brevis radix-like proteins; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; MKK3/6: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3/6; JIP4: JNK-interacting protein 4; ERK/1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2; Fyn: Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn; ATM: ATM serine/threonine kinase; c-Abl: tyrosine kinases c-Abl; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin; AKT1: RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase; PKA: protein kinase A; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinases; GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase 3β; CK1: casein kinase 1; TonE: tonicity-responsive enhancers; AP-1: activator protein-1; AR: aldose reductase; SMIT: sodium/myo-inositol transporter; TauT: taurine transporter; Hsp70: heat shock protein 70; iNos: inducible nitric oxide synthase; Ifnb: interferon β.