Figure 4-. Ethanol Drinking Does Not Alter Synaptic Transmission Onto CeA PDYN Neurons.
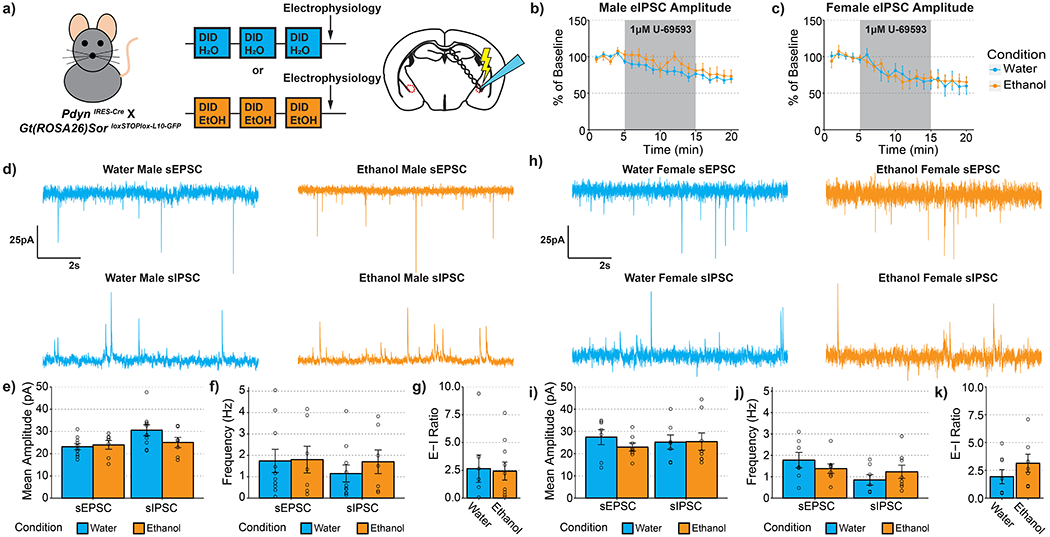
(a) Experimental timeline. (b) U69593 inhibition of eIPSCs is unaltered by a history of alcohol drinking in males t(9.391)=0.687, p=0.508. (c) U69593 inhibition of eIPSCs is also unaltered by a history of alcohol drinking in females t(14.880)=0.054, p=0.957. (d-g) Synaptic transmission in male animals. (d) Representative traces of excitatory and inhibitory events onto CeA dynorphin neurons. (e) Ethanol drinking did not alter the amplitude of excitatory t(11.152)=0.334, p=0.745 or inhibitory transmission t(14.704)=1.644, p=0.121. (f) Ethanol drinking did not alter the frequency of excitatory transmission t(13.390)=0.075, p=0.941 or inhibitory transmission t(11.767)=0.815, p=0.431. (g) synaptic drive was also unaltered after alcohol drinking t(10.982)=0.153, p=0.881. (h-k) Synaptic transmission in female animals. (h) Representative traces of excitatory and inhibitory events onto CeA dynorphin neurons. (i) Ethanol drinking did not alter the amplitude of excitatory transmission t(9.164)= 1.170, p=0.272 or inhibitory transmission t(12.847)=0.046, p=0.964. (j) Ethanol drinking did not alter the frequency of excitatory transmission t(10.198)=0.966, p=0.356 or inhibitory transmission t(12.731)=0.950, p=0.359. (k) synaptic drive was also unaltered after alcohol drinking t(11.806)=1.182, p=0.260. (b) Water male n=9 cells, N=6 mice, ethanol male n=7 cells, n=4 mice; (c) water female n=7 cells, N=5 mice, ethanol female n=6 cells, n=4 mice; (d-g) water male n=10 cells, n=6 mice, ethanol male n=9 cells, n=4 mice; (h-k) water female n=7 cells, n=4 mice, ethanol female n=8 cells, n=5 mice
