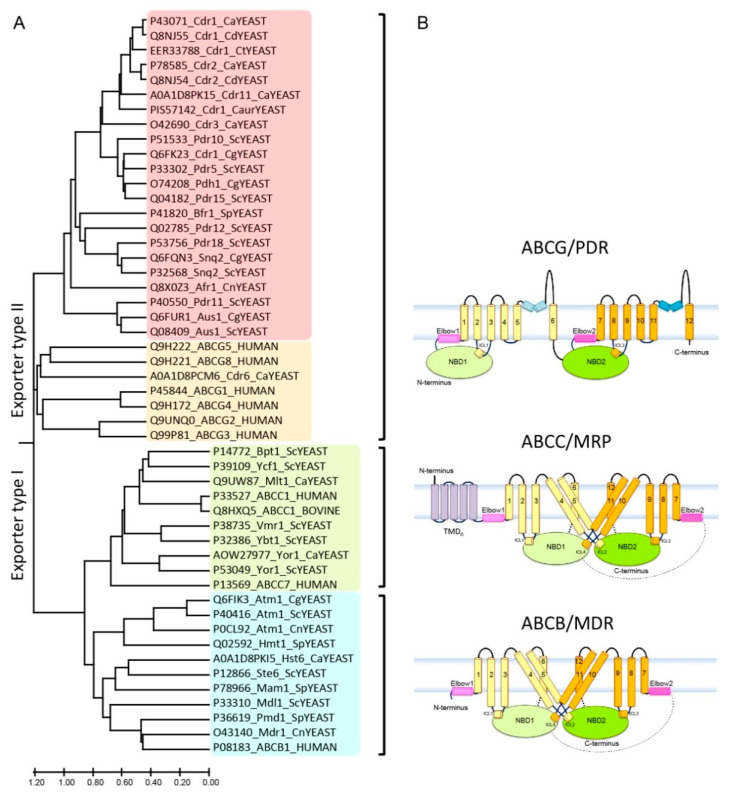
Figure 1.
Phylogeny and structural organization of ABC transporters in mammals and yeast. (A) The phylogenetic tree shows the evolutionary relationships of ABC transporter subfamilies in yeast and mammals. Some 29 ABC transporters were subjected to amino acid sequence alignments. Branch length was analyzed using MEGA-X, and represents the evolutionary distance in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. Names are given in the UniProt code, protein name and organism, respectively. The analysis reveals two major exporters subfamilies referred to as type I and II. Type I was sub-classified into ABCB/MDR (blue) and ABCC/MRP (green) subgroups. The type II family represents ABCG/PDR subgroups with the fungal (red) and mammalian transporters (orange). Ca: Candida albicans, Cg: Candida glabrata, Caur: Candida auris, Cd: Candida dubliniensis, Ct: Candida tropicalis, Cn: Cryptococcus neoformans, Sc: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Sp: Schizosaccharomyces pombe. (B) Predicted membrane topologies of three MDR ABC exporter families. The transporters hold several diagnostic hallmark domains, including two NBDs (NBD1: light green; NBD2: green), two TMD regions usually with 6 putative membrane-spanning helices each (TMD1: light yellow; TMD2: bright orange), elbow helix (pink), re-entry helix (blue) and TMD0 (purple), respectively.