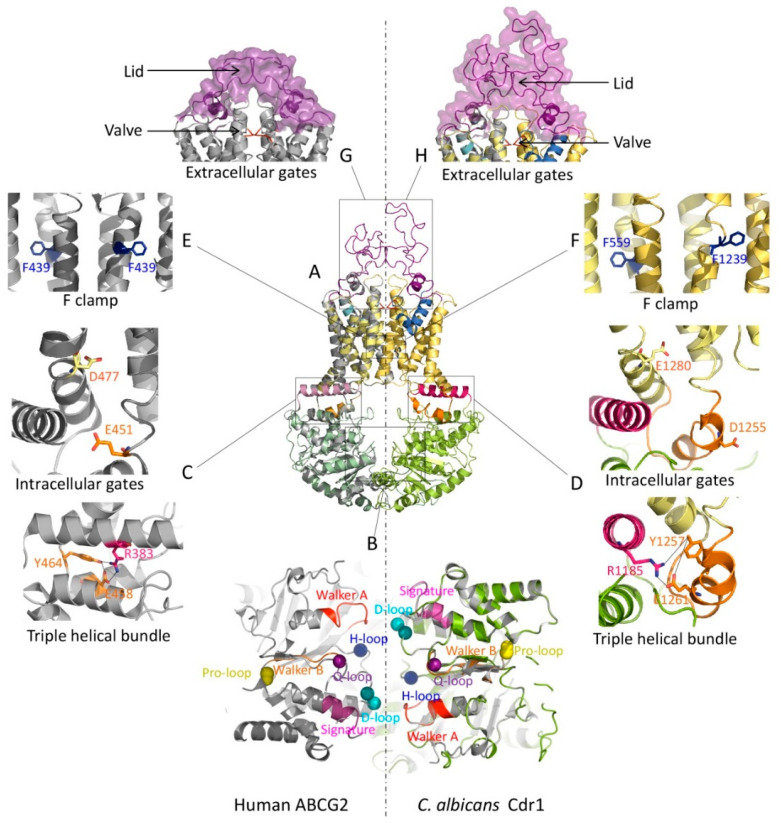
Figure 3.
Type II mammalian and fungal ABCG/PDR exporters share functional domains. (A) A homology model of the PDR exporter Cdr1 from C. albicans was generated using the SWISS-MODEL tool (color ribbon, NBD: green, TMD: yellow, elbow helix: pink, ICL: orange, valve: red, re-entry helix: blue and ECL: purple). The Cdr1 model was superimposed with the cryo-EM structure of human ABCG2 (PDB ID: 6VXF) (gray ribbon). (B) Zoom-in top view of the NBD dimer from panel A at the NBD–NBD interface shows essential conserved motifs (Walker A: red, Q-loop: violet, signature: pink, Pro-loop: yellow, Walker B: orange, D-loop: cyan and H-loop: blue). The transmission interfaces of human ABCG2 (C) and C. albicans Cdr1 (D) show a network cluster of triple helical bundles (THB) with conserved tyrosine residues as part of a salt bridge between elbow helix and ICL. Two negative residues are shown as the intracellular gates. Conserved residues are shown as sticks with color-coding as in the topology model. The conserved phenylalanine F clamp F439 in human ABCG2 (E) and the putative F clamp in C. albicans Cdr1 (F) are indicated as sticks. At the extracellular gates, the valve-like structures at the top of central cavity (red) are shown at the corresponding position of human ABCG2 (G) and C. albicans Cdr1 (H). The lid-structure formed by ECLs is shown as a violet ribbon with a surface. The homo-dimeric human ABCG2 transporter has a symmetric lid (G), while the full-size C. albicans Cdr1 transporter has a larger ECL forming the outer lid and part of the roof architecture (H).