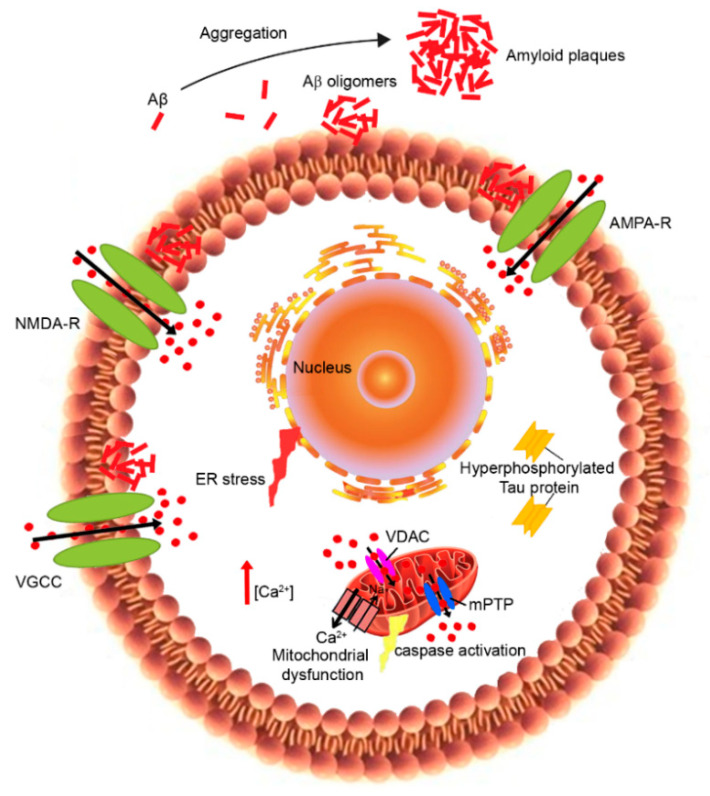
Figure 2.
Effects of Aβ and hyperphosphorylated tau protein on Ca2+ dysregulation and neuronal dysfunction in AD pathogenesis. Aβ oligomers formed in the extracellular space are able to interact with the plasma membrane, causing the hyperactivation of the calcium channels (NMDAR, AMPAR and VGCC). On the other hand, the intracellular hyperphosphorylated tau protein may promote Ca2+ dyshomeostasis. Overall, the increase in cytosolic Ca2+ levels results in mitochondrial dysfunction and the subsequent activation of the apoptotic cell death and ER stress.