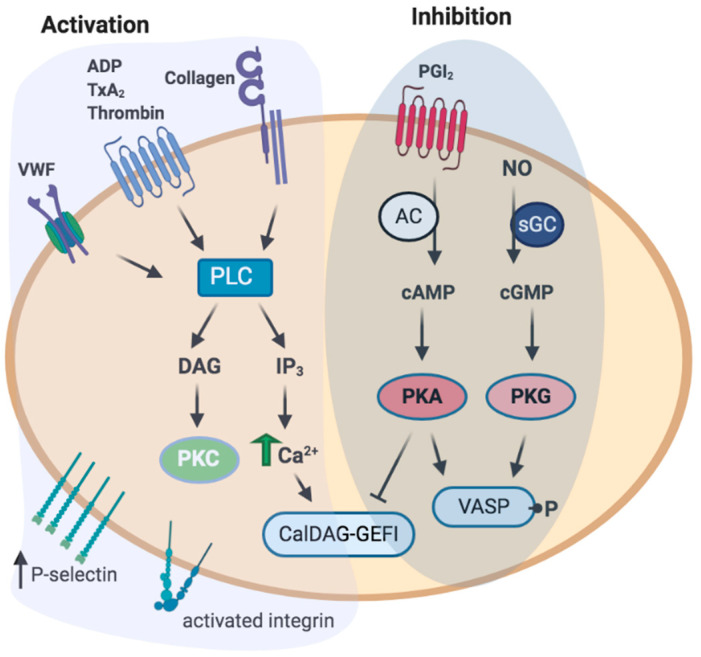
Figure 2.
Platelet activation and inhibition. Stimulation with major platelet agonists (ADP, TxA2, thrombin, collagen, VWF) activates phospholipase C (PLC), and increases downstream signals, resulting in increased P-selectin expression and integrin activation. Major inhibitory signals include prostacyclin I2 (PGI2), and nitric oxide (NO), that increase cAMP, or cGMP, resulting in the activated protein kinase A (PKA), or protein kinase G (PKG), respectively. PKA and PKG phosphorylate multiple downstream targets, e.g., VASP, or CalDEG–GEFI and, thus, mediate negative effect on platelet activation. Tight regulation of signaling pathways leading to the activation or inhibition of platelets is required for their proper function. Abbreviations: VWF, Von Willebrand Factor; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; TxA2, thromboxane A2; PLC, phospholipase C; DAG, diacylglycerol; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; PKC, protein kinase C; PGI2, prostacyclin I2; NO, nitric oxide; AC, adenylyl cyclase; sGC, soluble guanylyl cyclase; PKA, protein kinase A; PKG, protein kinase G; VASP, vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein.