FIG 1.
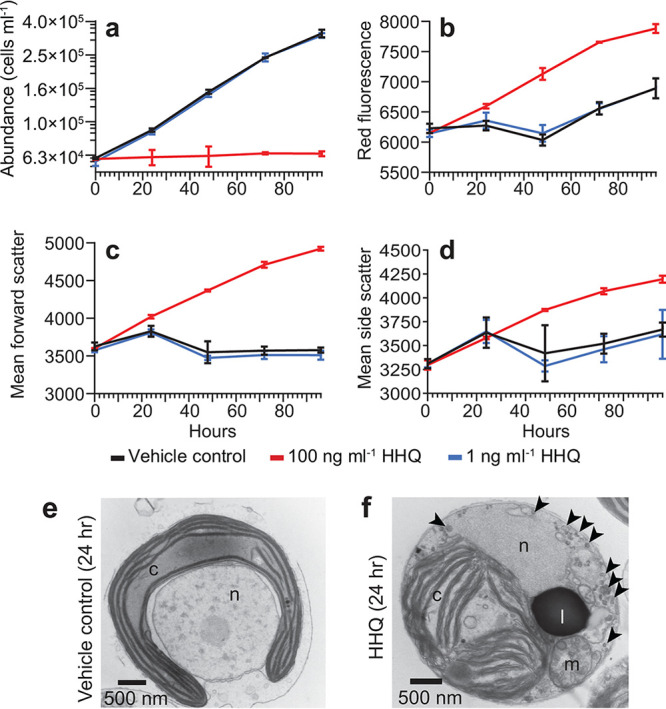
Exposure to HHQ halts cell division and alters cell morphology. (a through d) E. huxleyi cultures (n = 3) were exposed to HHQ or the vehicle control (DMSO) at the 0-h time point (T0) and monitored by flow cytometry for cell abundance (a), red fluorescence in relative fluorescence units (RFU) (695/50 nm) (a proxy for chlorophyll a intensity) (b), forward scatter (a proxy for cell size) (c), and side scatter (a proxy for cell granularity) (d) over 96 h. Means ± standard deviations are shown. In 100-ng ml−1 HHQ-exposed cells, all parameters measured were significantly different from those for the vehicle control (P < 0.05 by repeated-measures analysis of variance). Note that in panel a, data for HHQ-treated cells at 1 ng ml−1 sit directly beneath data for the vehicle control (DMSO). (e and f) Transmission electron microscopy micrographs of E. huxleyi cells exposed to the vehicle control (DMSO) (e) or 100 ng ml−1 HHQ (f) for 24 h. Subcellular structures include the chloroplast (c), lipid droplet (l), mitochondria (m), nucleus (n), and vacuoles (black arrowheads).
