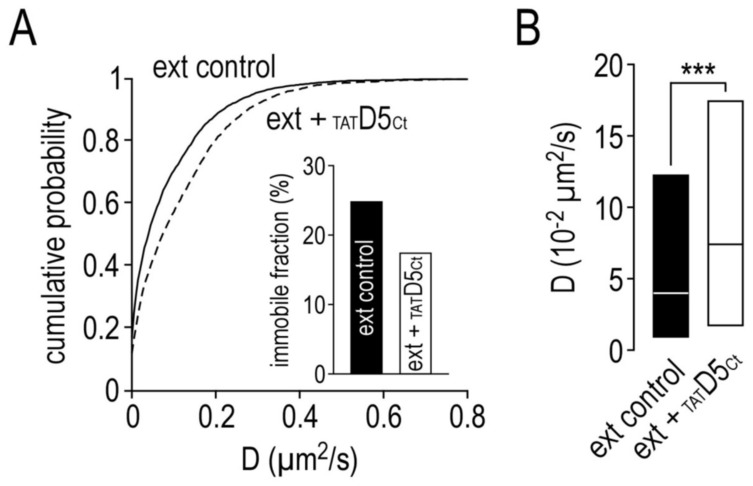
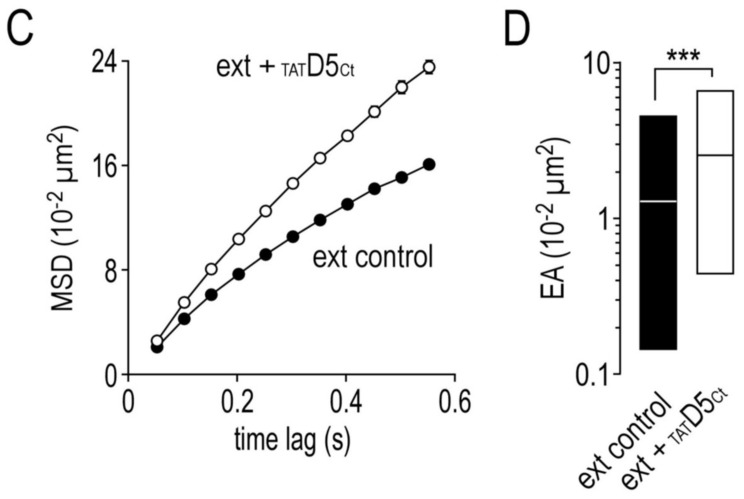
Figure 6.
The disrupting peptide also affects the surface dynamic properties of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors. (A) Cumulative probability diffusion coefficient of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in control condition or in the presence of the disrupting peptide (10 µM). The inset shows the immobile fraction (defined as D < 0.005 µm2/s) of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in control condition and in the presence of the disrupting peptide. (B) Bar graphs illustrating the instantaneous diffusion coefficient (D, represented as median ± interquartile range 25–75%) of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in control condition or in the presence of the disrupting peptide. (C) Comparison of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors mean square displacements (MSD, represented as mean ± SEM) in control condition or in the presence of the disrupting peptide. (D) Bar graphs illustrating the explored surface area (EA, represented as median ± interquartile range 25–75%) of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in control condition or in the presence of the disrupting peptide. *** p < 0.001. Nonparametric Mann–Whitney test.