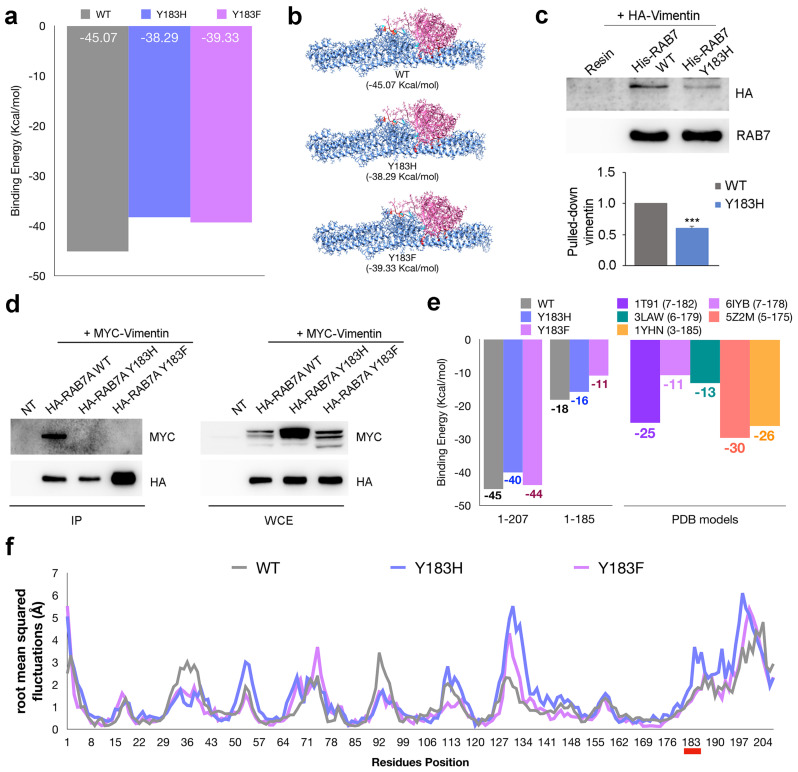
Figure 3.
Interaction between vimentin and the RAB7AY183 mutant proteins. (a) results of docking between vimentin and wild type or mutated RAB7A. (b) 3D structure of the complexes between vimentin and RAB7A wild type, Y183H or Y183F obtained by Gramm-X docking simulations. (c) bacterially expressed and purified His-tagged RAB7A wild type and Y183H were incubated with total extracts of HeLa cells overexpressing HA-vimentin and pulled down with Ni-NTA resin. Proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-HA and anti-RAB7A antibodies. Quantification of pulled-down vimentin is shown. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments. *** = p < 0.001. (d) HA-tagged RAB7A wild type, Y183H or Y183F and myc-tagged vimentin wild type proteins were expressed in HeLa cells. IP has been performed using anti-HA resin. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-myc and anti-HA antibodies. Protein expression in the lysates before performing co-IP has been checked (WCE). (e) Left: results of simulations of Gramm-X docking using RAB7A complete models (1-207) and RAB7A truncated models (1-185); Right: results of PatchDock simulations using as ligands different models of RAB7A downloaded from the PDB (RSCB) database. In the legend start and stop residues for each model are shown. (f) fluctuation plots obtained performing CABSflex analysis on RAB7A wild type and Y183H and Y183F mutant models.