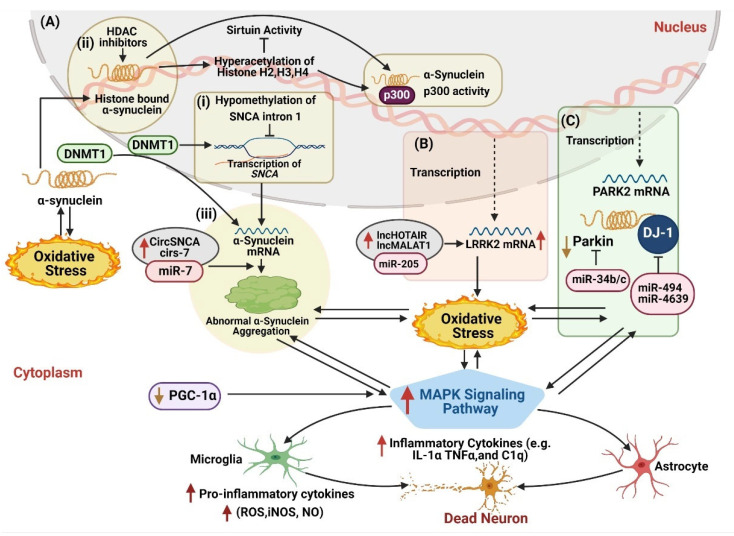
Figure 3.
The landscape of synergic epigenetic interactions with MAPK signaling pathway in PD development. (A) MAPK signaling pathway is activated due to abnormal accumulation of α-synuclein, which activates glial cells and inflammatory cytokines. (i) Hypomethylation of the intron 1 of SNCA locus dysregulates SNCA gene transcription, leading to abnormal α-synuclein aggregation in the cytoplasm. This allows abnormal α-synuclein to enter the nucleus following oxidative stress and sequester DNMT1 into the cytoplasm, enhancing the hypomethylation of SNCA gene and causing dysregulated transcription. (ii) Meanwhile, HDAC inhibitors cause hyperacetylation of α-synuclein linked histones H2, H3, H4, and p300 promoter region of SNCA to induce α-synuclein aggregation. (iii) Synergic interaction of DNMT1, circSNCA, and cirs-7a suppresses miR-7 expression, which upregulated SNCA gene expression to trigger α-synuclein accumulation. (B) Similarly, LncHOTAIR1 and lncMALAT1 interact with miR-205 to overexpress LRRK2 and activates MAPK signaling pathway. (C) miR-34b/c interacts with PARK2 and DJ-1 to inhibit their neuroprotective role and activates glia cells. miR-494 and miR-4639 downregulate DJ-1 activity and upregulate nitric oxide ten folds to promote neuroinflammation. Moreover, lower expression of PGC-1α also contributes to MAPK signaling pathway activation. Altogether, these epigenetic mechanisms interact with each other and with MAPK signaling pathways to induce neuroinflammation in PD development. Note: ↓ shows downregulated expression, and ↑ shows an upregulated expression.