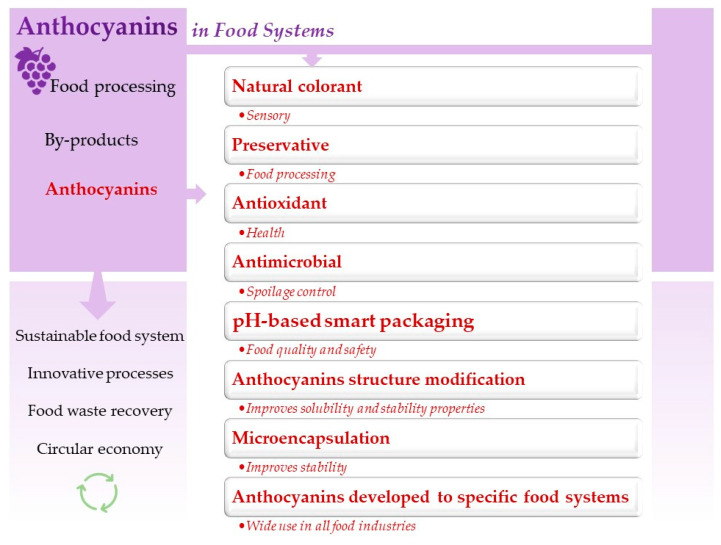
Figure 3.
Anthocyanins can be recovered from food agri-food by-products. It is an important strategy to improve the food chain, especially to develop a sustainable food system, by using innovative processes and a food waste recovery approach. The second part of this figure (right) brings the anthocyanin uses commonly described by literature and industry, such as natural colorants, preservatives, antioxidants, antimicrobials, and health-promoting agents, as well as the innovative uses recently described in scientific reports; for instance, the pH anthocyanin-based smart packaging, and anthocyanin structure modification. Microencapsulation with macromolecules, such as proteins and polysaccharides, has been reported to enhance the anthocyanins’ stability during food processing and storage and over the human gastrointestinal digestion system. Food systems present different behavior and, as a consequence, the food technologists should carefully develop anthocyanin formulations appropriate to these specific systems using, for example, the strategies presented herein. Certainly, novel purposes will appear over time about these multi-property biomolecules. Nevertheless, the literature data clearly demonstrate that the food industry may extensively explore anthocyanins as food additives and functional ingredients.