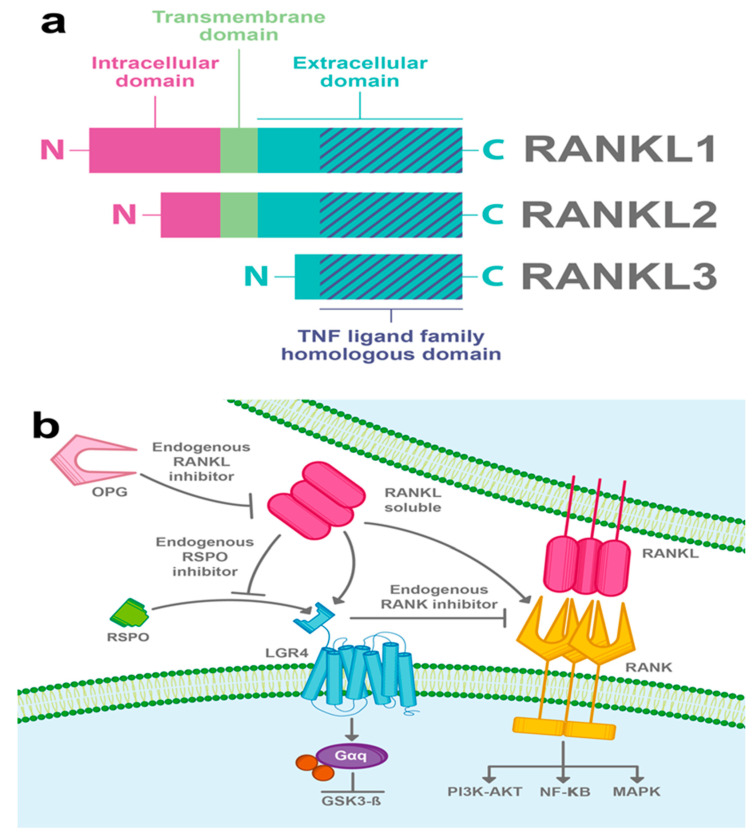
Figure 3.
RANKL-induced LGR4 signaling pathway. (a) RANKL is another molecule that can promote LGR4 activity. Three isoforms of RANKL have been described; the full-length RANKL (RANKL1), a form lacking part of the intra-cytoplasmic domain (RANKL2), and a soluble form (RANKL3). All three isoforms have a TNF ligand family homologous domain in their extracellular part. (b) RANKL interacts with LGR4 and induces the Gαq protein pathway and also inhibits GSK3β. Furthermore, RANKL activates RANK and promotes NF-κB canonical RANK signaling among other pathways, for instance; PI3K-AKT and MAPK. LGR4 competes with RANK to bind RANKL and suppresses canonical RANK signaling. Besides, it has been suggested that RANKL can compete with RSPOs to bind LGR4 and in this way disrupt RSPO-induced Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) acts as a RANKL endogenous inhibitor.