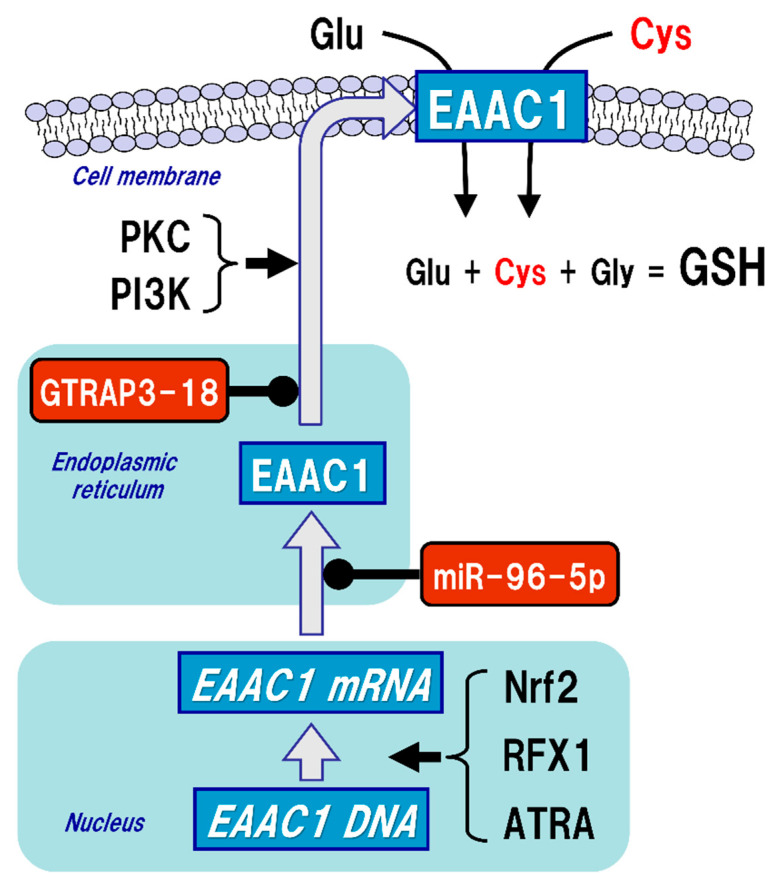
Figure 3.
Regulation of excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1) expression. Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide synthesized from glutamate (Glu), cysteine (Cys), and glycine (Gly). Neuronal GSH synthesis relies on intracellular Cys but not Glu or Gly level. Cys uptake (red font) is subjected to the regulation of both gene expression and post-translational modifications of EAAC1 under facilitative (arrow) and suppressive (black circles) controls. EAAC1 gene expressions are promoted by nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), regulatory factor X1 (RFX1), and all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA). Protein kinase C (PKC) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) activations increase the EAAC1 expression on the plasma membrane. Glu transporter-associated protein 3-18 (GTRAP3-18) and miR-96-5p post-translationally suppress the protein expression of EAAC1, leading to decreased Cys uptake and subsequently decreased GSH synthesis in neurons.