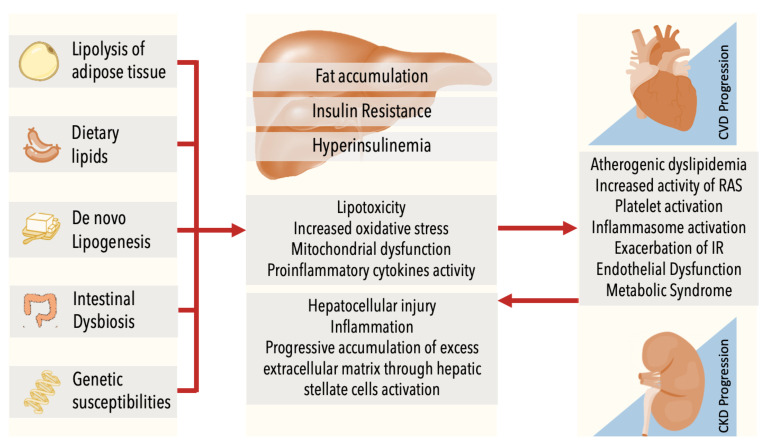
Figure 1.
NAFLD, CKD and CVD share common risk factors. Lipolysis of adipose tissue, dietary lipids, de novo lipogenesis, dysbiosis and genetic susceptibilities act in parallel, contributing to fat accumulation. It leads to insulin resistance (IR), enhancing liver trygliceride accumulation and results in compensatory hyperinsulinemia which increases the hepatic fatty acid uptake, alters triglycerides transportation and inhibits liver β-oxidation. There is an intensification of the pro-inflammatory cytokine activity that is associated with oxidative stress-mediated lipotoxicity, increased activity of RAS, platelet activation, inflammasome activation and mitochondrial dysfunction. These processes contribute to further exacerbation of IR, hepatocellular injury, inflammation and the progressive accumulation of excess extracellular matrix through hepatic stellate cells activation. NAFLD: Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, CKD: Chronic Kidney Disease; CVD: Cardiovascular Disease; IR: insulin resistance; RAS: renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.