Figure 1.
Production of high-affinity and specific mAb against SARS-CoV-2 NP using wheat germ cell-free synthesized antigen
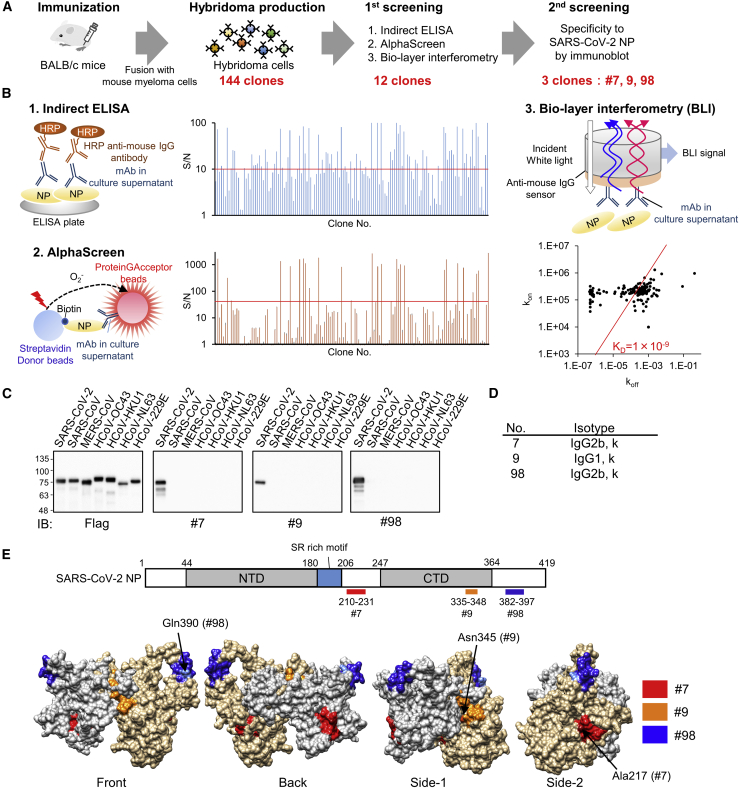
(A) Schematic diagram of hybridoma cells production to generate anti-SARS-CoV-2-NP mAb. Purified protein was injected into BALB/c mice. After 4 weeks, lymphocytes from immunized mice were fused with myeloma cells, and 144 hybridoma cells were established.
(B) Of the 144 clones, the 12 that exhibited high reactivity to antigen proteins, as revealed by indirect ELISA, AlphaScreen, and Bio-layer interferometry, were selected for further investigation (two technical replicates). Red line indicates cutoff line of screening; S/N = 10 for ELISA, S/N = 40 for AlphaScreen, and KD = 1.0 × 109. kon and koff values for each antibody clones to the ΔN-NP antigen estimated by OctetRED96 instrument using hybridoma supernatant are indicated as dots on the two-dimensional plot.
(C) Specificity screening of mAbs. FLAG-glutathione S-transferase (GST)-tagged NPs derived from several human coronaviruses were produced in the wheat germ extract system. Reactivity of generated mAbs was validated by immunoblot analysis using either anti-FLAG or the indicated antibodies. Three clones specifically detect SARS-CoV-2 NP and were selected (representative data of two technical replicates).
(D) Isotype of selected mAbs.
(E) Schematic diagram of SARS-CoV-2-NP domain architecture and epitopes of antibodies. CTD, C-terminal domain; LKR, flexible linker region; NTD, N-terminal domain. Positions of epitopes in a structural model of whole-length dimer-forming NP, constructed by homology modeling using partial structures of SARS-CoV-2 NP are shown (PDB: 6yun; PDB: 6m3m). Epitope localizations of each mAb on molecular surface are highlighted in different colors. Critical residues for the specificity of mAb were indicated by arrows.