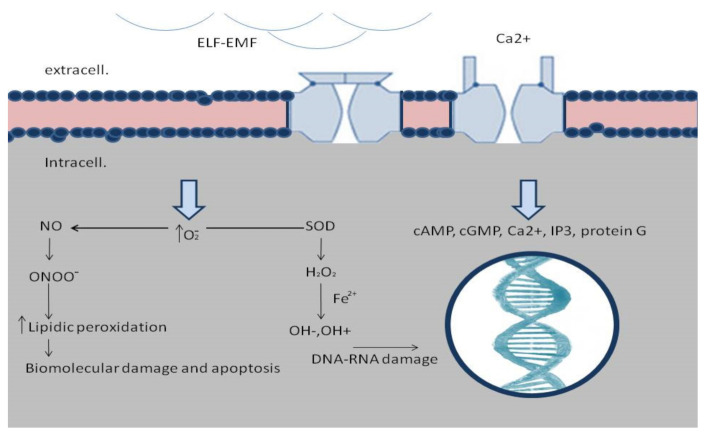
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms of ELF-EMFs’ effects on cell function. ELF-EMFs open voltage-dependent calcium channels, causing interference in cell differentiation with Ca2+ influx into cells. It is well documented that Ca2+ ions affect activity-dependent gene expression, and this effect is mediated by signaling pathways activating Ca2+-responsive DNA regulatory elements. Decreasing antioxidants concentration has a defense mechanism against free radicals. The ELF-EMFs could also induce the production of oxygen (O2) in the cellular environment, which plays a major role in oxidative damage that, subsequently, led to biomolecular damage, DNA double strand breaks, DNA/RNA damage, and cell death.