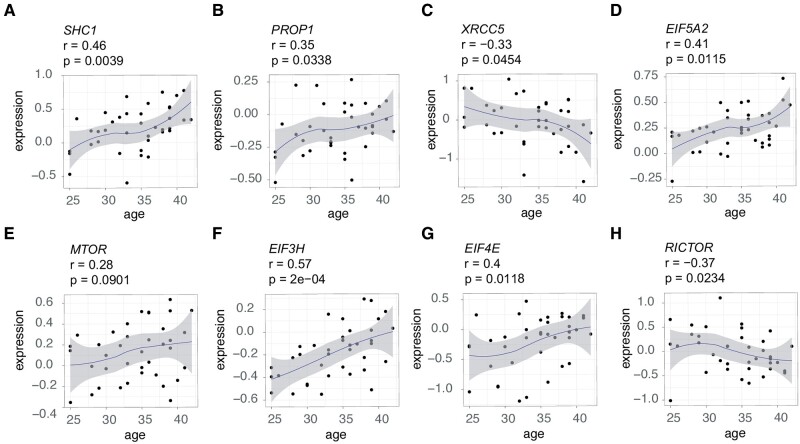
Figure 3.
Gene expression levels in germinal vesicle oocytes from women of different ages. (A–D) Correlation of mRNA expression levels of selected genes with age. Genes were selected based on the observation that they changed in an opposite direction to what would be required for a longevity benefit. This includes (A) an increase in SHC adaptor protein 1 (SHC1), (B) an increase in PROP paired-like homeobox 1 (PROP1), (C) a decrease in the DNA repair related gene X-ray repair cross complementing 5 (XRCC5), and (D) an increase in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2). (E–H) Expression levels in oocytes with age of a selection of ‘growth’-related genes involved in ageing and longevity. Genes were selected to highlight that multiple other genes in the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway are upregulated in ovarian ageing. This includes (E) MTOR itself, (F) EIF3H, (G) EIF4E, and (H) EIF5A2. Gene expression levels are relative expression from microarray data of oocytes, from Smits et al. (2018). Age designates the donor’s age in years. Correlations (r) and P values (P) between individuals’ ages and ranked expression data were assessed using Pearson's product moment correlation coefficient.