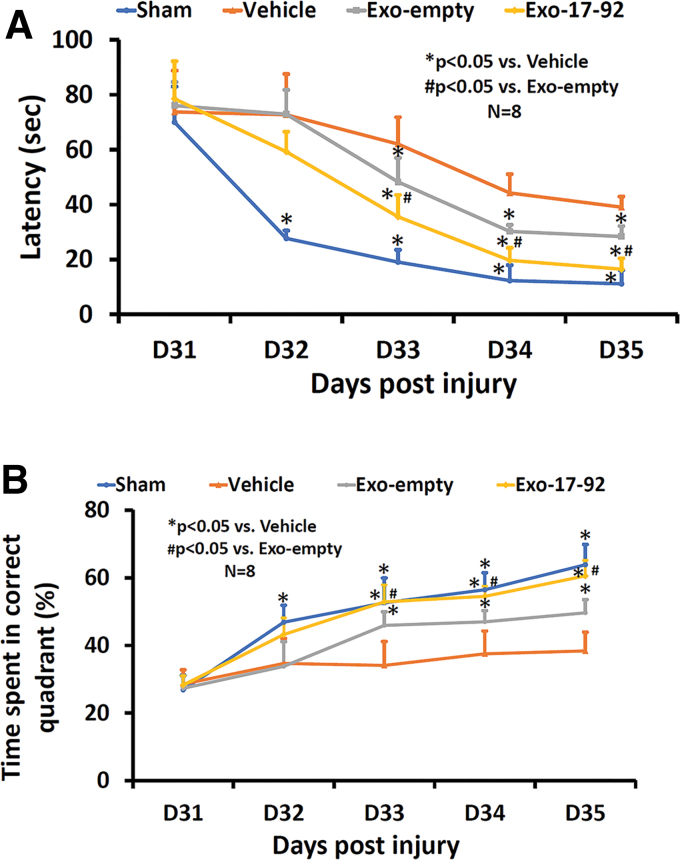
FIG. 2.
Treatment with exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) significantly improves spatial learning and memory in the Morris water maze (MWM) test measured by latency to find the hidden platform in the correct quadrant by rats after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Both Exo-empty and Exo-17-92 treatments administered intravenously 24 h after TBI reduced the latency to reach the hidden platform starting at 33 days (A) and increasing the percentage of time spent in the correct quadrant where the hidden platform was located (B) in the MWM testing compared with Vehicle treatment. Compared with the Exo-empty, Exo-17-92 exhibited significantly better effects on reducing the latency and increasing the percentage of time (A and B). Data represent mean ± standard deviation. N = 8/group. Color image is available online.