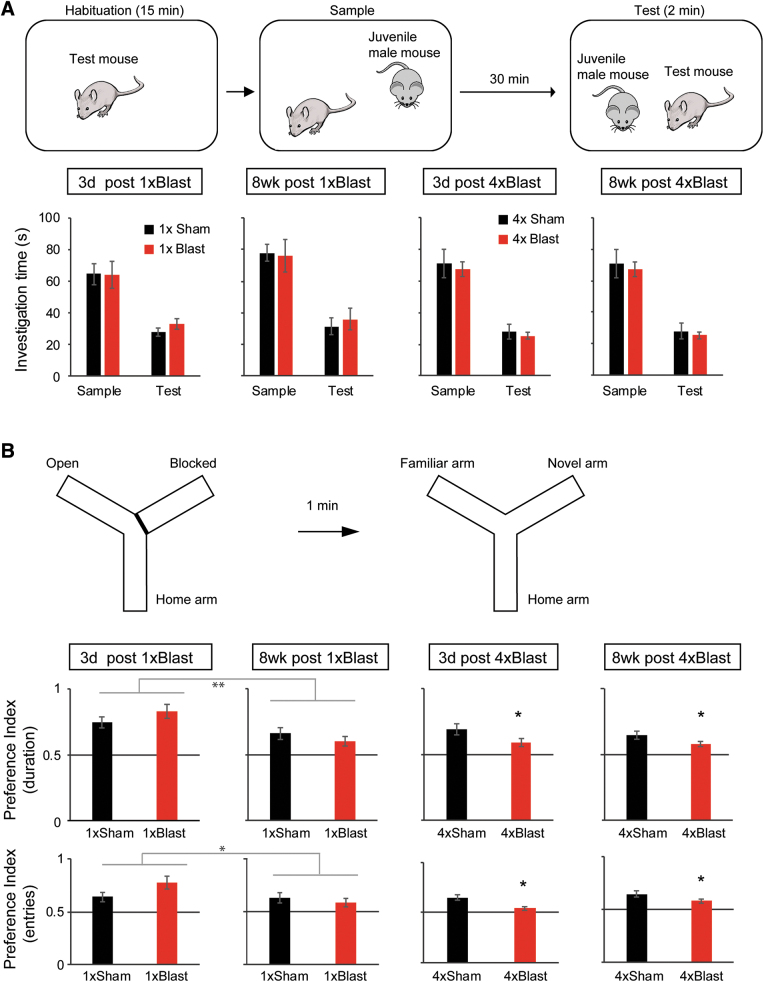
FIG. 6.
bTBI impaired spatial novelty preference, but not social recognition. (A) Schematic illustration of the social recognition test (top) and accompanying results (bottom). Blast and Sham mice showed similar reductions in social investigation duration during the test trial, as compared to the sample trial. (B) Schematic illustration of spontaneous spatial novelty preference Y-maze test (top) and accompanying results (bottom). Preference indices for the novel arm, as measured by both duration (top graph row) and #entries (bottom graph row), showed a significant main effect of blast for 1 × Blast and for 4 × Blast. Preference index (duration) was above chance for Blast and Sham mice at all time points. Preference index (#entries) was above chance for Blast and Sham mice at time points except 8 weeks for 1 × Blast and 3 days for 4 × Blast mice. **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05. The number of mice for both the social recognition and Y-maze tests were: n = 7 for 1 × Sham and n = 7 for 1 × Blast for 3 days, n = 7 for 1 × Sham and n = 7 for 1 × Blast at 8 weeks, n = 11 for 4 × Sham and n = 9 for 4 × Blast at 3 days, and n = 7 for 4 × Sham and n = 5 for 4 × Blast at 8 weeks. Data are mean ± SEM. bTBI, blast traumatic brain injury; SEM, standard error of the mean. Color image is available online.