Figure 1.
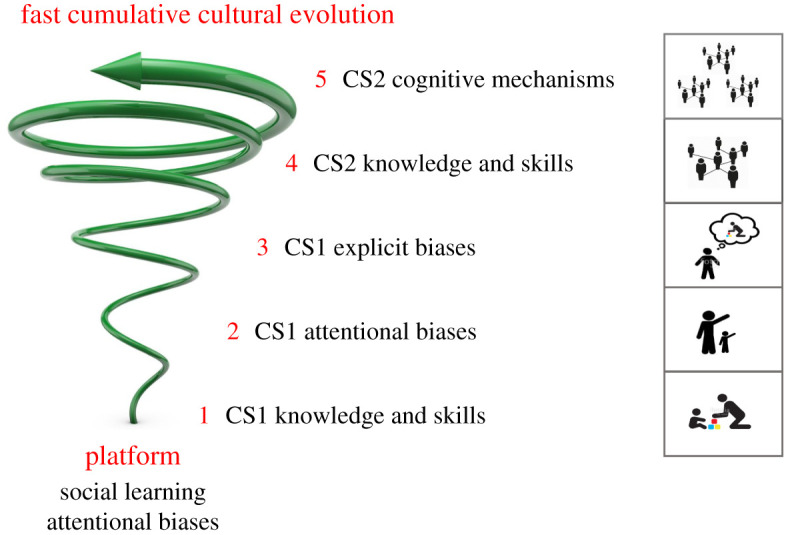
The self-assembly hypothesis. Culture–culture coevolution produces fast cumulative culture in five steps. CS1 initiates the coevolutionary process. First knowledge and skills (Step 1), then attentional social learning biases (Step 2), then explicit social learning biases (Step 3), are socially inherited from biological parents and spread through the population because their bearers tend to have more offspring. Subsequently, CS2 also contributes. Enhanced knowledge and skills (Step 4) and cognitive mechanisms (Step 5) are socially inherited from unrelated individuals and spread through the population because some models are more successful than others in competition for learners. The five-step process not only produces fast cumulative culture, but is itself cumulative: each step augments, rather than replaces, the previous step (spiral arrow). The schematic figures on the right represent typical social interactions in each step. See text for details. (Online version in colour.)
