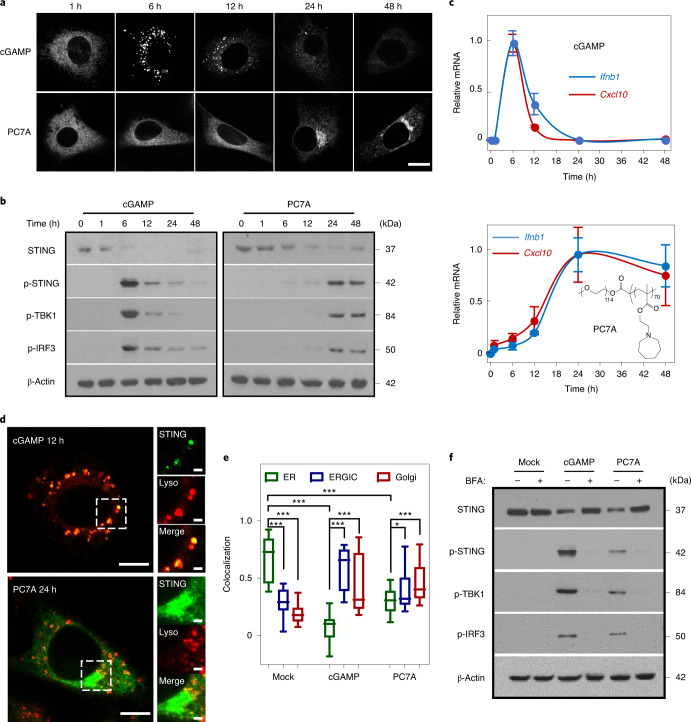
Fig. 1. PC7A polymer activates STING with a spatiotemporal profile that is distinct from cGAMP.
a, MEFs primed by cGAMP or PC7A exhibit different geometric and temporal patterns of GFP–STING-punctate formation and depletion. Cells were first incubated with cGAMP (10 μM, PEI was used for cytosolic delivery; Supplementary Fig. 1a,b) or PC7A micelles (10 μM) for 1 h, and the medium was then exchanged and cells were incubated for the indicated periods before imaging. Scale bar, 10 μm. b, THP1 cells that were treated with cGAMP display a burst effect of TBK1/IRF3 phosphorylation followed by rapid STING degradation, whereas treatment with PC7A led to sustained TBK1/IRF3 phosphorylation and slower STING degradation. c, Relative Ifnb1 and Cxcl10 mRNA levels show slower but prolonged STING activation in THP1 cells by PC7A compared with cGAMP. Data are mean ± s.d. n = 3 biologically independent experiments. d, GFP–STING colocalizes with lysosomes in MEFs 12 h after cGAMP treatment, supporting rapid degradation. By contrast, PC7A inhibits lysosomal degradation of GFP–STING, as indicated by the lack of colocalization and persistent GFP fluorescence. Scale bars, 5 μm (left images); 1 μm (right images). e, cGAMP and PC7A induce similar STING translocation from the ER to the ERGIC and Golgi apparatus. Colocalization was quantified using the Pearson’s correlation coefficient. For the box plot, the centre line is the mean, the box limits show the 25th to 75th percentile, and the whiskers show the minimum and maximum values. n = 20 cells examined over three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using two-tailed Student’s t-tests (PC7A treatment group: ER versus ERGIC, *P = 0.029; ER versus Golgi, ***P = 0.0005; for all other comparisons, ***P < 0.0001). f, STING translocation is necessary for downstream signalling as BFA, which is an inhibitor of protein transport from ER to Golgi, prevents the phosphorylation of TBK1/IRF3 by cGAMP or PC7A. The confocal images in a and d are representative of at least three biologically independent experiments.