Fig. 12. Schlemm’s canal inlet valve attachments to SC external wall at collector channel entrances.
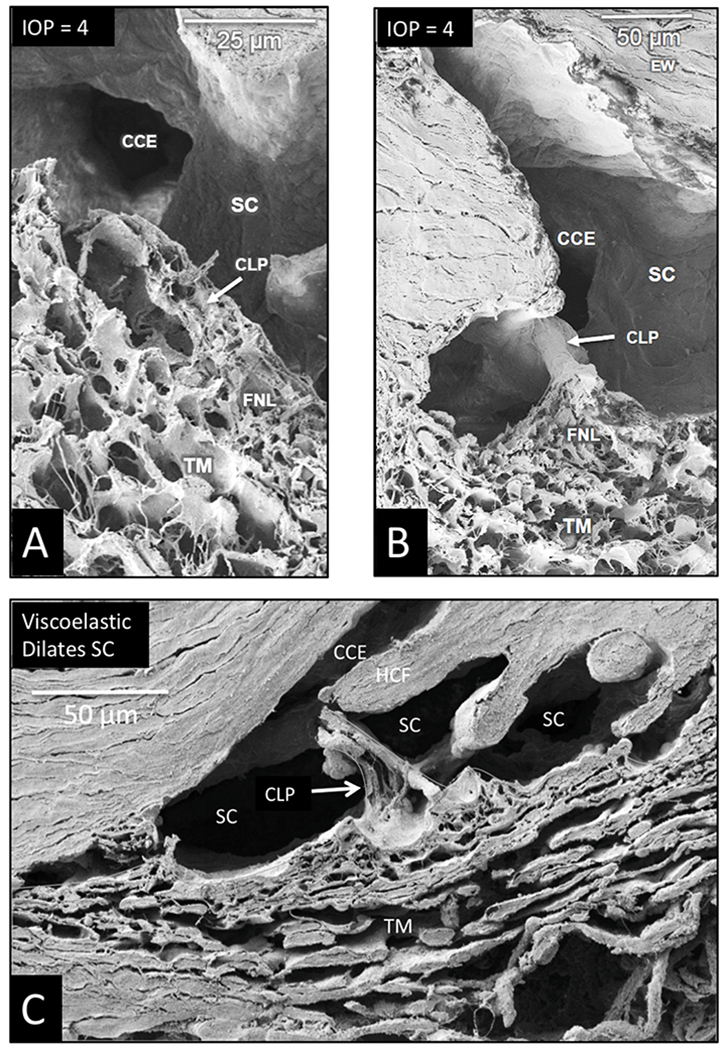
Scanning electron microscopy images (A, B) are from an eye with an IOP of 4 mm Hg during fixation. An SC inlet valve has a funnel shaped (FNL) region as it joins the trabecular meshwork (TM). The funnel region leads to a cylindrical area that crosses SC to attach at collector channel entrances (CCE). The section in (A) bisects the SC inlet valve lumen of the conduit-like pathway (CLP), revealing the lumen connection between the funnel-shaped juxtaeanalieular space and collector channel entrance. Internal structural features are like those of the juxtaeanalieular space. (B) A view of the funnel region of a Schlemm’s inlet valve with a plane of section revealing its surface features as it courses across the canal from the TM to SC external wall at the entrance of a collector channel. (C) Viscoelastic dilated Schlemm’s canal (SC) before fixation. The image reveals the conduit-like pathway (CLP) of the Schlemm’s canal inlet valve as it arises from the TM and attaches to a hinged collagen flap (HCF) at SC external wall. The inlet valve is bisected, revealing an open distal end in communication with a collector channel entrance (CCE). Aqueous can flow freely into SC and CCE through the lumen of the conduit-like pathways. Tissue source: Primate, Macaca nemestrina. From the Johnstone Glaucoma Lab, University of Washington.
