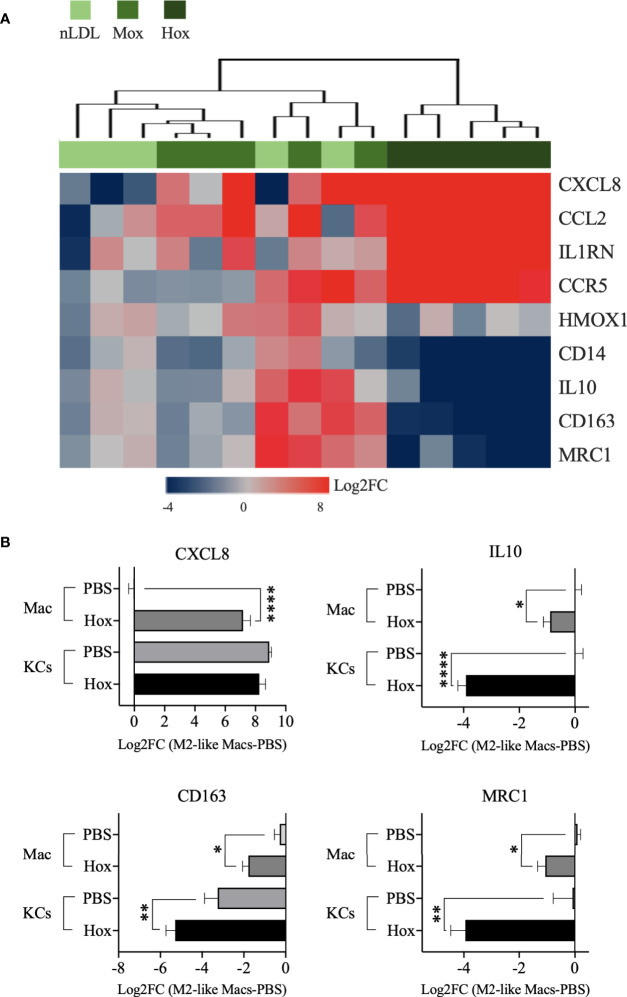
Figure 3.
M2-like macrophages and Kupffer cells stimulated by HoxLDL switch to the M4-like proinflammatory phenotype. (A) Heatmap displays the M4-biomarkers expressed by M2-like macrophages exposed to nLDL, MoxLDL, and HoxLDL (values = Log2FC compared to PBS, n=5). Genes from the HoxLDL group follow the M4 profile, with upregulation of CXCL8, CCL2, CCR5, and IL1RN, and downregulation of CD14, CD163, HMOX1, MRC1, and IL10, suggesting that M2-like macrophages stimulated by HoxLDL change into the proinflammatory M4 phenotype. All the genes are significantly changed in the HoxLDL group. (B) Among the M4 biomarkers, we measured the expression of CXCL8, IL10, CD163, and MRC1 in human KCs with and without HoxLDL stimulation. Compared to in vitro M2-like differentiated macrophages (n=5), KCs (n=5) are high constitutive producers of CXCL8, not changing significantly after HoxLDL exposure. However, the other common KCs’ markers were significantly downregulated after HoxLDL treatment, indicating that KCs may shift to the M4-like phenotype in the presence of HoxLDL as well. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. One way ANOVA test; *p <0.05, **p <0.01, ****p <0.0001.